Necrotising otitis externa: A single centre experience
- PMID: 33505446
- PMCID: PMC7814081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joto.2020.07.005
Necrotising otitis externa: A single centre experience
Abstract
Introduction: Necrotising otitis externa (NOE) is a rare infection of the ear canal with frequent bone erosion. This study's objective is to describe the different features of NOE as well as its management in an ear-nose-throat department. We also tried to identify the particularities of the fungal infection.
Patients and methods: It is an observational cohort that included all the patients hospitalised for the management of NOE. The study was carried out in the ear-nose-throat Department of Mahdia University Hospital in Tunisia between January 2006 and december 2019.
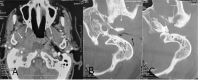
Results: A total of 40 patients were included. The mean age was 65 ± 12.9 years and the sex ratio was 0.9. Ninety percent of the patients included were diabetics. The most common signs found were oedema of the external canal (97.5%) and auricular discharge (92.5%). The main pathogen isolated was Pseudomonas aeruginosa (61.7%). Fungi were isolated in 9 cases (26.47%). Computed tomography was performed for 32 patients (80%). Bone erosion was seen in 26 cases (81.3%). The main complications were cerebral venous thrombosis, retropharyngeal abscess and cerebral empyema. Thirty one patients received only antibiotics, 2 received only antifungal treatment, and 7 received both antibiotics and antifungal treatment. All patients had a favorable outcome. Univariate analysis showed a higher median erythrocyte sedimentation rate was associated with fungal infections. No other differences were noted.
Conclusion: Our management protocol seems to be efficient since all patients had initial favorable outcome. A higher median erythrocyte sedimentation rate was associated with fungal infections.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Fungi; Otitis externa; Pseudomonas; Therapeutics.
© 2020 PLA General Hospital Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. Production and hosting by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this manuscript to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Bray C., Bell L.N., Liang H., Haykal R., Kaiksow F., Mazza J.J., Yale S.H. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein measurements and their relevance in clinical medicine. Wis. Med. J. 2016;115:317–321. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

