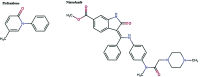
Antifibrotic drugs in connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD): from mechanistic insights to therapeutic applications
- PMID: 33505482
- PMCID: PMC7813437
- DOI: 10.7573/dic.2020-8-6
Antifibrotic drugs in connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD): from mechanistic insights to therapeutic applications
Abstract
Fibrosing interstitial lung disease (ILD) is one of the most important causes of morbidity and mortality in patients with connective tissue diseases (CTDs), which include systemic sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, idiopathic inflammatory myositis and systemic lupus erythematosus. The treatment of CTD-ILDs is challenging due to the paucity of proven effective treatments. Recently, two antifibrotic drugs conditionally approved for use in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, nintedanib and pirfenidone, have been trialled in CTD-ILDs based on overlapping pathological and clinical features between the two diseases. In this narrative review, we discuss the experimental evidence and clinical trials investigating the efficacy and safety of antifibrotic drugs in patients with CTD-ILDs and the potential mechanisms of action involved. Results from clinical trials suggest that nintedanib use retards lung function decline in progressive fibrotic CTD-ILDs. By contrast, the evidence for the efficacy of pirfenidone in these groups is not equally compelling. Further, well-designed randomized clinical trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of individual antifibrotic drugs in specific CTD-ILD subgroups.
Keywords: Sjögren’s syndrome; connective tissue diseases; idiopathic inflammatory myopathies; interstitial lung disease; nintedanib; pirfenidone; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic sclerosis.
Copyright © 2021 Erre GL, Sebastiani M, Manfredi A, Gerratana E, Atzeni F, Passiu G, Mangoni AA.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and potential conflicts of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) Potential Conflicts of Interests form for the authors is available for download at: https://www.drugsincontext.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/dic.2020-8-6-COI.pdf
Figures
References
-
- Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188(6):733–748. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources