Analyzing Surgical Treatment of Intestinal Obstruction in Children with Artificial Intelligence
- PMID: 33505514
- PMCID: PMC7814945
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6652288
Analyzing Surgical Treatment of Intestinal Obstruction in Children with Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
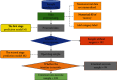
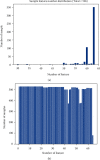
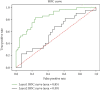
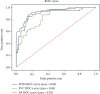
Intestinal obstruction is a common surgical emergency in children. However, it is challenging to seek appropriate treatment for childhood ileus since many diagnostic measures suitable for adults are not applicable to children. The rapid development of machine learning has spurred much interest in its application to medical imaging problems but little in medical text mining. In this paper, a two-layer model based on text data such as routine blood count and urine tests is proposed to provide guidance on the diagnosis and assist in clinical decision-making. The samples of this study were 526 children with intestinal obstruction. Firstly, the samples were divided into two groups according to whether they had intestinal obstruction surgery, and then, the surgery group was divided into two groups according to whether the intestinal tube was necrotic. Specifically, we combined 63 physiological indexes of each child with their corresponding label and fed them into a deep learning neural network which contains multiple fully connected layers. Subsequently, the corresponding value was obtained by activation function. The 5-fold cross-validation was performed in the first layer and demonstrated a mean accuracy (Acc) of 80.04%, and the corresponding sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), and MCC were 67.48%, 87.46%, and 0.57, respectively. Additionally, the second layer can also reach an accuracy of 70.4%. This study shows that the proposed algorithm has direct meaning to processing of clinical text data of childhood ileus.
Copyright © 2021 Wang-Ren Qiu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Ileus and intestinal obstruction].Nihon Rinsho. 2013 Jun;71(6):1027-30. Nihon Rinsho. 2013. PMID: 23855208 Review. Japanese.
-
Ileus and intestinal obstruction--comparison between children and adults.Pol Przegl Chir. 2011 Jul;83(7):367-71. doi: 10.2478/v10035-011-0058-9. Pol Przegl Chir. 2011. PMID: 22166664
-
Artificial Intelligence Algorithm-Based Computed Tomography Images in the Evaluation of the Curative Effect of Enteral Nutrition after Neonatal High Intestinal Obstruction Operation.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Nov 16;2021:7096286. doi: 10.1155/2021/7096286. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9793864. doi: 10.1155/2023/9793864. PMID: 34824765 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Developing a Recognition System for Diagnosing Melanoma Skin Lesions Using Artificial Intelligence Algorithms.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 May 15;2021:9998379. doi: 10.1155/2021/9998379. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34055044 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanical ileus in children with no prior history of abdominal surgery].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2015;159:A8911. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2015. PMID: 26443112 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Potential and Promise: Artificial Intelligence in Pediatric Surgery.J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2024 Sep-Oct;29(5):400-405. doi: 10.4103/jiaps.jiaps_88_24. Epub 2024 Aug 23. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2024. PMID: 39479435 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Surgery: A Systematic Review of Use and Validation.J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 24;13(23):7108. doi: 10.3390/jcm13237108. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39685566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications in Emergency Surgery: A Systematic Review of Diagnostic Accuracy and Clinical Outcomes.Cureus. 2025 Jun 5;17(6):e85386. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85386. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40621368 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical