Nrf2-ARE Signaling Partially Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mammary Lesions via Regulation of Oxidative and Organelle Stresses but Not Inflammatory Response in Mice
- PMID: 33505589
- PMCID: PMC7810562
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8821833
Nrf2-ARE Signaling Partially Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mammary Lesions via Regulation of Oxidative and Organelle Stresses but Not Inflammatory Response in Mice
Abstract
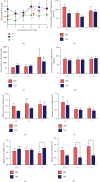
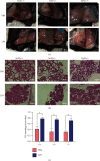
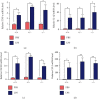
The incidence of mastitis is high during the postpartum stage, which causes severe pain and hinders breast feeding in humans and reduces milk production in dairy cows. Studies suggested that inflammation in multiple organs is associated with oxidative stress and nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-antioxidant response element pathway is one of the most important antioxidant pathways, but the effects of Nrf2 on antioxidation in the mammary gland during mastitis are still unclear. In this study, intramammary lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge was carried out in wild-type (WT) and Nrf2 knockout mice. Results showed that the expression of Nrf2 affected the expression of milk protein genes (Csn2 and Csn3). Importantly, LPS treatment increased the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 and the content of glutathione in the mammary gland of WT mice, but not in Nrf2(-/-) mice. The expression levels of glutathione synthesis genes (GCLC, GCLM, and xCT) were lower in Nrf2(-/-) mice than in WT mice. Moreover, mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic and endoplasmic reticulum stress were significantly relieved in WT mice compared with that in Nrf2(-/-) mice. In summary, the expression of Nrf2 may play an important role in prevention of oxidative and organelle stresses during endotoxin-induced mastitis in mouse mammary gland.
Copyright © 2021 Yongxin Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

