Vascular calcification of chronic kidney disease: A brief review
- PMID: 33505876
- PMCID: PMC7821827
- DOI: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_36_20
Vascular calcification of chronic kidney disease: A brief review
Abstract
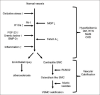
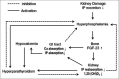
Vascular calcification (VC) is highly prevalent among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). There is growing evidence that there is more underlying this condition than the histological presentation of atherosclerotic plaque and arteriosclerosis and that the risk of cardiovascular disease in the context of CKD might be explained by the presence of VC. While VC has been observed in the absence of overt abnormal mineral metabolism, this association is coupled to abnormal homeostasis of minerals in patients with CKD, due to hyperphosphatemia and hypercalcemia. Furthermore, recent studies have shown that the differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells into an osteogenic phenotype is highly regulated by pro-calcifying and anti-calcifying factors. There are several imaging modalities currently used in clinical practice to evaluate the extent and severity of VC; each has different advantages and limitations. Although there is no universally accepted method for the treatment of VC, there is growing evidence of the beneficial effects of medical therapy for the condition. This study discusses the mechanism underlying VC, imaging modalities used for evaluation of the condition, and possible treatments.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Chronic kidney disease; Image; Treatment; Vascular calcification.
Copyright: © 2020 Tzu Chi Medical Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Amann K. Media calcification and intima calcification are distinct entities in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:1599–605. - PubMed
-
- Bild DE, Detrano R, Peterson D, Guerci A, Liu K, Shahar E, et al. Ethnic differences in coronary calcification: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) Circulation. 2005;111:1313–20. - PubMed
-
- Goodman WG, Goldin J, Kuizon BD, Yoon C, Gales B, Sider D, et al. Coronary-artery calcification in young adults with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1478–83. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
