Recent Progress in Quantitatively Monitoring Vesicular Neurotransmitter Release and Storage With Micro/Nanoelectrodes
- PMID: 33505953
- PMCID: PMC7831278
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.591311
Recent Progress in Quantitatively Monitoring Vesicular Neurotransmitter Release and Storage With Micro/Nanoelectrodes
Abstract
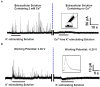
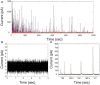
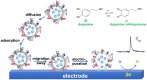
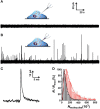
Exocytosis is one of the essential steps for chemical signal transmission between neurons. In this process, vesicles dock and fuse with the plasma membrane and release the stored neurotransmitters through fusion pores into the extracellular space, and all of these steps are governed with various molecules, such as proteins, ions, and even lipids. Quantitatively monitoring vesicular neurotransmitter release in exocytosis and initial neurotransmitter storage in individual vesicles is significant for the study of chemical signal transmission of the central nervous system (CNS) and neurological diseases. Electrochemistry with micro/nanoelectrodes exhibits great spatial-temporal resolution and high sensitivity. It can be used to examine the exocytotic kinetics from the aspect of neurotransmitters and quantify the neurotransmitter storage in individual vesicles. In this review, we first introduce the recent advances of single-cell amperometry (SCA) and the nanoscale interface between two immiscible electrolyte solutions (nanoITIES), which can monitor the quantity and release the kinetics of electrochemically and non-electrochemically active neurotransmitters, respectively. Then, the development and application of the vesicle impact electrochemical cytometry (VIEC) and intracellular vesicle impact electrochemical cytometry (IVIEC) and their combination with other advanced techniques can further explain the mechanism of neurotransmitter storage in vesicles before exocytosis. It has been proved that these electrochemical techniques have great potential in the field of neuroscience.
Keywords: amperometry; electrodes; exocytosis; neurotransmitter; vesicle; vesicle impact electrochemical cytometry (VIEC).
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Du, Wang, Zhang, Liu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
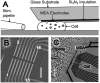
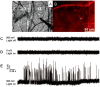
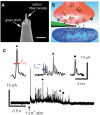
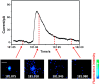




Similar articles
-
Intracellular injection of phospholipids directly alters exocytosis and the fraction of chemical release in chromaffin cells as measured by nano-electrochemistry.Chem Sci. 2020 Oct 6;11(43):11869-11876. doi: 10.1039/d0sc03683h. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 34123212 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Vesicle Electrochemistry Reveals Polysaccharide from Glochidion eriocarpum Champ. Regulates Vesicular Storage and Exocytotic Release of Dopamine.Anal Chem. 2024 Sep 11. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c02493. Online ahead of print. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39262202
-
Quantitative Chemical Measurements of Vesicular Transmitters with Electrochemical Cytometry.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Oct 18;49(10):2347-2354. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00331. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 27622924
-
From Insulin Measurement to Partial Exocytosis Model: Advances in Single Pancreatic Beta Cell Amperometry over Four Decades.ACS Meas Sci Au. 2024 Oct 10;4(6):629-637. doi: 10.1021/acsmeasuresciau.4c00058. eCollection 2024 Dec 18. ACS Meas Sci Au. 2024. PMID: 39713028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical Quantification of Neurotransmitters in Single Live Cell Vesicles Shows Exocytosis is Predominantly Partial.Chembiochem. 2021 Mar 2;22(5):807-813. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000622. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Chembiochem. 2021. PMID: 33174683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Catecholamines in sepsis: pharmacological insights and clinical applications-a narrative review.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2025 Apr 3;5(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s44158-025-00241-2. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2025. PMID: 40176108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-Vesicle Microelectroanalysis Reveals the Role of PIP2 Phospholipid in Vesicle Opening Dynamics and Its Potential Role in Exocytosis.ACS Omega. 2025 May 1;10(18):18889-18898. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00864. eCollection 2025 May 13. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40385141 Free PMC article.
-
Simulations of amperometric monitoring of exocytosis: moderate pH variations within the cell-electrode cleft with the buffer diffusion.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021 Nov;413(27):6769-6776. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03443-z. Epub 2021 Jun 13. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021. PMID: 34120197
-
New Opportunities of Electrochemistry for Monitoring, Modulating, and Mimicking the Brain Signals.JACS Au. 2023 Aug 9;3(8):2062-2072. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00220. eCollection 2023 Aug 28. JACS Au. 2023. PMID: 37654584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Updated Review on Electrochemical Nanobiosensors for Neurotransmitter Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 19;13(9):892. doi: 10.3390/bios13090892. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

