Extracellular Vesicle-Derived microRNA-410 From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protects Against Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Brain Damage Through an HDAC1-Dependent EGR2/Bcl2 Axis
- PMID: 33505958
- PMCID: PMC7829500
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.579236
Extracellular Vesicle-Derived microRNA-410 From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protects Against Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia Brain Damage Through an HDAC1-Dependent EGR2/Bcl2 Axis
Abstract
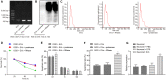
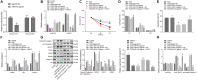
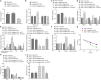
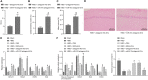
Hypoxia-ischemia brain damage (HIBD) is a neurological disorder occring in neonates, which is exacerbated by neuronal apoptosis. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) have been proposed as a promising strategy for treating or preventing ischemia-related diseases. However, their mechanisms in HIBD remain unclear. Thus, we aimed to address the role of EV-derived microRNA (miR)-410 in HIBD. Neonatal HIBD mouse model was constructed using HI insult, from which neurons were isolated, followed by exposure to oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD). EVs were isolated from human umbilical cord (hUC)-derived MSCs. In silico analyses, dual-luciferase reporter gene and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were adopted to determine relationships among miR-410, histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), early growth response protein 2 (EGR2), and B cell lymphoma/leukemia 2 (Bcl2). The functional roles of EV-derived miR-410 were determined using loss- and gain-of functions experiments, and by evaluating neuronal viability, cell-cycle distribution and neuronal apoptosis in vitro as well as modified neurological severity score (mNSS), edema formation, and cerebral infarction volume in vivo. hUC-MSCs-derived EVs protected against HIBD in vivo and inhibited the OGD-induced neuronal apoptosis in vitro. miR-410 was successfully delivered to neurons by hUC-MSCs-EVs and negatively targeted HDAC1, which inversely mediated the expression of EGR2/Bcl2. Upregulation of EV-derived miR-410 promoted the viability but inhibited apoptosis of neurons, which was reversed by HDAC1 overexpression. EV-derived miR-410 elevation reduced mNSS, edema formation, and cerebral infarction volume by increasing EGR2/Bcl2 expression through downregulating HDAC1 expression in vivo. In summary, EV-derived miR-410 impeded neuronal apoptosis by elevating the expression of EGR2/Bcl2 via HDAC1 downregulation, thereby providing a potential strategy for treating or preventing HIBD.
Keywords: Bcl2; early growth response 2; extracellular vesicle; histone deacetylase 1; microRNA-410; neonatal hypoxia-ischemia brain damage.
Copyright © 2021 Han, Yang, Hao, Zhang, Zhang, Xin and Hao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neuroprotection of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Enclosed miR-410 Correlates with HDAC4 Knockdown in Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage.Neurochem Res. 2022 Oct;47(10):3150-3166. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03670-5. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 36028735
-
Overexpressed microRNA-539-5p inhibits inflammatory response of neurons to impede the progression of cerebral ischemic injury by histone deacetylase 1.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Aug 1;319(2):C381-C391. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00576.2019. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. Retraction in: Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Nov 1;319(5):C945. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00576.2019_RET. PMID: 32491927 Retracted.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicle-enclosed microRNA-93 Prevents Hypoxic-ischemic Brain Damage in Rats.Neuroscience. 2022 Sep 15;500:12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.06.037. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Neuroscience. 2022. PMID: 35803492
-
microRNA-93 packaged in extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells reduce neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.Brain Res. 2022 Nov 1;1794:148042. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2022.148042. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 35952773
-
Umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells co-modified by TERT and BDNF: a novel neuroprotective therapy for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2014 Nov;38:147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2014.06.014. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24999119 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of extracellular vesicle microRNA clusters in developing healthy and Rett syndrome brain organoids.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Sep 21;81(1):410. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05409-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39305343 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of antenatal administration of stem cell derived extracellular vesicles in the brain of rat fetuses with congenital diaphragmatic hernia.Pediatr Surg Int. 2023 Nov 13;39(1):291. doi: 10.1007/s00383-023-05578-9. Pediatr Surg Int. 2023. PMID: 37955723
-
Neuroprotection of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Enclosed miR-410 Correlates with HDAC4 Knockdown in Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage.Neurochem Res. 2022 Oct;47(10):3150-3166. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03670-5. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 36028735
-
Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles and Perinatal Injury: One Formula for Many Diseases.Stem Cells. 2022 Nov 29;40(11):991-1007. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxac062. Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 36044737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA-Guided Regulation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from the Umbilical Cord: Paving the Way for Stem-Cell Based Regeneration and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 24;24(11):9189. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119189. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Evran S., Calis F., Akkaya E., Baran O., Cevik S., Katar S., et al. (2020). The effect of high mobility group box-1 protein on cerebral edema, blood-brain barrier, oxidative stress and apoptosis in an experimental traumatic brain injury model. Brain Res. Bull. 154 68–80. 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.10.013 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

