Peroxisomal Metabolite and Cofactor Transport in Humans
- PMID: 33505966
- PMCID: PMC7829553
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.613892
Peroxisomal Metabolite and Cofactor Transport in Humans
Abstract
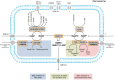
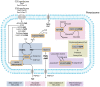
Peroxisomes are membrane-bound organelles involved in many metabolic pathways and essential for human health. They harbor a large number of enzymes involved in the different pathways, thus requiring transport of substrates, products and cofactors involved across the peroxisomal membrane. Although much progress has been made in understanding the permeability properties of peroxisomes, there are still important gaps in our knowledge about the peroxisomal transport of metabolites and cofactors. In this review, we discuss the different modes of transport of metabolites and essential cofactors, including CoA, NAD+, NADP+, FAD, FMN, ATP, heme, pyridoxal phosphate, and thiamine pyrophosphate across the peroxisomal membrane. This transport can be mediated by non-selective pore-forming proteins, selective transport proteins, membrane contact sites between organelles, and co-import of cofactors with proteins. We also discuss modes of transport mediated by shuttle systems described for NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH. We mainly focus on current knowledge on human peroxisomal metabolite and cofactor transport, but also include knowledge from studies in plants, yeast, fruit fly, zebrafish, and mice, which has been exemplary in understanding peroxisomal transport mechanisms in general.
Keywords: carrier; cofactor; exchanger; membrane contact sites; metabolism; peroxisomes; transporter.
Copyright © 2021 Chornyi, IJlst, van Roermund, Wanders and Waterham.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Peroxisomal Cofactor Transport.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 12;10(8):1174. doi: 10.3390/biom10081174. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32806597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transport proteins regulate the flux of metabolites and cofactors across the membrane of plant peroxisomes.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Jan 16;3:3. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00003. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22645564 Free PMC article.
-
The solute carrier SLC25A17 sustains peroxisomal redox homeostasis in diverse mammalian cell lines.Free Radic Biol Med. 2024 Feb 20;212:241-254. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.12.035. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38159891
-
Transfer of metabolites across the peroxisomal membrane.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep;1822(9):1374-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.12.011. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22206997 Review.
-
Peroxisomal membrane permeability and solute transfer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Dec;1763(12):1697-706. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.08.044. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 17045662 Review.
Cited by
-
High-content image screening to identify chemical modulators for peroxisome and ferroptosis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Feb 17;29(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00544-2. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38368371 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating transitions during the evolution of specialised peroxisomes: Glycosome formation in kinetoplastid and diplonemid protists.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 12;10:979269. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.979269. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36172271 Free PMC article.
-
Pexophagy and Oxidative Stress: Focus on Peroxisomal Proteins and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Signaling Pathways.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jan 23;14(2):126. doi: 10.3390/antiox14020126. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of transmembrane protein 135 in mitochondrial and peroxisomal functions - implications for age-related retinal disease.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024;4:1355379. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2024.1355379. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38576540 Free PMC article.
-
The peroxisomal transporter ABCD3 plays a major role in hepatic dicarboxylic fatty acid metabolism and lipid homeostasis.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021 Nov;44(6):1419-1433. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12440. Epub 2021 Oct 2. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021. PMID: 34564857 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

