The Differential Diagnosis of Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides and Vitiligo With Reflectance Confocal Microscopy: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 33505981
- PMCID: PMC7829195
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.609404
The Differential Diagnosis of Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides and Vitiligo With Reflectance Confocal Microscopy: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
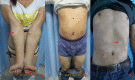
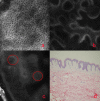
Objective: To investigate the role of reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) in the differential diagnosis of hypopigmented mycosis fungoides (HMF) and vitiligo. Methods: Cases with persistent hypopigmented patches, suspicious of early stage vitiligo, or HMF were imaged with RCM. The melanin contents and inflammatory conditions of the epidermis and superficial dermis of the lesions were compared with the same layers of the adjacent skin, and then, the imaged lesions were biopsied and analyzed by histology. Results: 15 cases were enrolled in this study, and based on the RCM findings, there was just slight or moderate reduction of melanin but no melanin absence in the basal cell layer of HMF lesions. The finding of monomorphous weakly refractile, oval to round cells on the basis of vesicle-like dark space was clearly elucidated in the epidermis of the lesions by RCM, which indicates the Pautrier's microabscesses on histopathology. Among those 15 cases, 13 cases were identified as HMF, and the other two cases were vitiligo, based on RCM findings, which were confirmed by histology analysis. Conclusions: The RCM findings correlated well with histology results in the screening of HMF, which indicates the RCM is an important tool in the early detection and differential diagnosis of HMF.
Keywords: detection; differential daignosis; hypo-pigmented mycosis fungoides; imaging; reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM); vitiligo.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Wang, Lin, Shan and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy of mycosis fungoides: A preliminary study.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007 Sep;57(3):435-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.02.026. Epub 2007 Apr 16. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17433849
-
Role of In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in the Analysis of Melanocytic Lesions.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Apr;26(1):64-67. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 29782304 Review.
-
Reflectance confocal microscopy for the characterization of mycosis fungoides and correlation with histology: a pilot study.Skin Res Technol. 2013 Aug;19(3):352-5. doi: 10.1111/srt.12049. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Skin Res Technol. 2013. PMID: 23594100
-
In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy imaging of vitiligo, nevus depigmentosus and nevus anemicus.Skin Res Technol. 2011 Nov;17(4):404-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0846.2011.00521.x. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Skin Res Technol. 2011. PMID: 21429011 Clinical Trial.
-
Progress in the application of reflectance confocal microscopy in dermatology.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021 Oct;38(5):709-715. doi: 10.5114/ada.2021.110077. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021. PMID: 34849113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-invasive skin measurement methods and diagnostics for vitiligo: a systematic review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 27;10:1200963. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1200963. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37575985 Free PMC article.
-
[Hypopigmented mycosis fungoide. Case report].Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2024 May 6;62(3):1-5. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.10998993. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2024. PMID: 39530859 Free PMC article. Spanish.
References
-
- Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, Moskowitz A, Querfeld C. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part I. Diagnosis: clinical and histopathologic features and new molecular and biologic markers. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2014) 70:205 10.1016/j.jaad.201307049 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

