Administration of All-Trans Retinoic Acid to Pregnant Sows Improves the Developmental Defects of Hoxa1-/- Fetal Pigs
- PMID: 33506002
- PMCID: PMC7829359
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2020.618660
Administration of All-Trans Retinoic Acid to Pregnant Sows Improves the Developmental Defects of Hoxa1-/- Fetal Pigs
Abstract
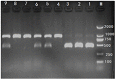
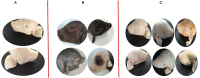
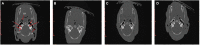
Hoxa1 mutation adversely affect fetal pig development, but whether all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) administration to Hoxa1+/- pregnant sows can improve Hoxa1-/- fetal pig development defects has not been reported. A total of 24 healthy Hoxa1+/- sows were mated with a healthy Hoxa1+/- boar and randomly assigned to one control group and nine experiment groups. ATRA was orally administered to pregnant sows at the doses of 0, 4, 5, or 6 mg/kg maternal body weight on 12, 13, and 14 days post coitum (dpc), respectively, and a total of 146 live piglets were delivered including 37 Hoxa1-/- piglets and 109 non-Hoxa1-/- piglets. Results indicated that Hoxa1-/- piglets delivered by sows in control group had bilateral microtia, canal atresia and ear's internal defects, and had lower birth liveweight and external ear score than non-Hoxa1-/- neonatal piglets (P < 0.05). Maternal administration with ATRA can effectively correct the development defects of Hoxa1-/- fetal pigs, Hoxa1-/- neonatal piglets delivered by sows administered ATRA at a dose of 4 mg/kg body weight on 14 dpc had higher birth liveweight (P > 0.05) and higher scores of external ear (P < 0.05) compared to Hoxa1-/- neonatal piglets from the control group, but had no significantly difference in terms of birth liveweight and external ear integrity than non-Hoxa1-/- piglets from the control group (P > 0.05). The time of ATRA administration significantly affected Hoxa1-/- fetal development (P < 0.05). Administration of ATRA to Hoxa1+/- pregnant sows at 4 mg/kg body weight on 14 dpc can effectively improve the birth liveweight and ear defects of Hoxa1-/- piglets.
Keywords: Hoxa1 mutation; all-trans retinoic acid; ear defects; fetal pig; intrauterine growth retardation.
Copyright © 2021 Zhou, Chen, Hu, Gao, Lu and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

