Comprehensive Analysis of the Profiles of Differentially Expressed mRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in Phosgene-Induced Acute Lung Injury
- PMID: 33506021
- PMCID: PMC7811572
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6278526
Comprehensive Analysis of the Profiles of Differentially Expressed mRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in Phosgene-Induced Acute Lung Injury
Abstract
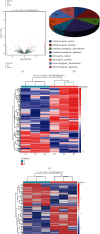
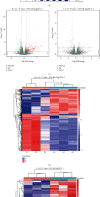
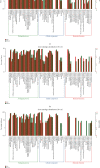
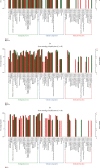
Phosgene exposure can cause acute lung injury (ALI), for which there is no currently available effective treatment. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) which have been proven to have therapeutic potential and be helpful in the treatment of various diseases, but the mechanisms underlying the function of MSCs against phosgene-induced ALI are still poorly explored. In this study, we compared the expression profiles of mRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in the lung tissues from rats of three groups-air control (group A), phosgene-exposed (group B), and phosgene + MSCs (group C). The results showed that 389 mRNAs, 198 lncRNAs, and 56 circRNAs were differently expressed between groups A and B; 130 mRNAs, 107 lncRNAs, and 35 circRNAs between groups A and C; and 41 mRNAs, 88 lncRNAs, and 18 circRNAs between groups B and C. GO and KEGG analyses indicated that the differentially expressed RNAs were mainly involved in signal transduction, immune system processes, and cancers. In addition, we used a database to predict target microRNAs (miRNAs) interacting with circRNAs and the R network software package to construct a circRNA-targeted miRNA gene network map. Our study showed new insights into changes in the RNA expression in ALI, contributing to explore the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic potential of MSCs in phosgene-induced ALI.
Copyright © 2021 Yiru Shao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Diller W. F. Pathogenesis of phosgene poisoning. Toxicology and Industrial Health. 2016;1:7–15. - PubMed
-
- van der Heijden M., van Nieuw Amerongen G. P., Chedamni S., van Hinsbergh V. W., Johan Groeneveld A. B. The angiopoietin-tie 2 system as a therapeutic target in sepsis and acute lung injury. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets. 2008;13:39–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

