Reduced Expression of Antimicrobial Protein Secretory Leukoprotease Inhibitor and Clusterin in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
- PMID: 33506054
- PMCID: PMC7810533
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/1057186
Reduced Expression of Antimicrobial Protein Secretory Leukoprotease Inhibitor and Clusterin in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
Abstract
Introduction: Antimicrobial peptides and proteins (AMPs) constitute the first line of defense against pathogenic microorganisms in the airway. The association between AMPs and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) requires further investigations. This study is aimed at investigating the expression and regulation of major dysregulated AMPs in the nasal mucosa of CRSwNP.
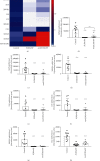
Methods: The expression of AMPs was analyzed in nasal tissue from patients with eosinophilic (E) CRSwNP and nonECRSwNP and healthy subjects using RNA sequencing. The 10 most abundant AMPs expressed differentially in CRSwNP patients were verified by real-time PCR, and of these, the expression and regulation of secretory leukoprotease inhibitor (SLPI) and clusterin (CLU) were investigated further.
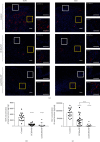
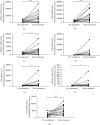
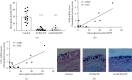
Results: The 10 most abundant AMPs expressed differentially in CRSwNP compared to healthy control, regardless of subtypes, included BPIFA1, BPIFB1, BPIFB2, CLU, LTF, LYZ, and SLPI, which were downregulated, and S100A8, S100A9, and HIST1H2BC, which were upregulated. ELISA and immunofluorescence confirmed the decreased expression of SLPI and CLU levels in CRSwNP. SLPI is expressed in both nasal epithelial cells and glandular cells, whereas CLU is mainly expressed in glandular cells. AB/PAS staining further demonstrated that both SLPI and CLU were mainly produced by mucous cells in submucosal glands. Furthermore, the numbers of submucosal glands were significantly decreased in nasal polyp tissue of CRSwNP compared to nasal tissue of controls. SLPI was downregulated by TGF-β1 and IL-4 in cultured nasal tissues in vitro, while CLU expression was inhibited by TGF-β1. Glucocorticoid treatment for 2 weeks significantly increased the expression of all downregulated AMPs, but not LYZ. Additionally, budesonide significantly increased the expression of SLPI and CLU in cultured nasal tissues.
Conclusion: The expression of major antimicrobial proteins is significantly decreased in nasal tissue of CRSwNP. The expression of SLPI and CLU is correlated with the numbers of submucosal glands and regulated by inflammatory cytokines and glucocorticoids.
Copyright © 2021 Yanran Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The antimicrobial protein short palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone 1 (SPLUNC1) is differentially modulated in eosinophilic and noneosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Feb;133(2):420-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.09.052. Epub 2013 Dec 15. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24342548
-
Epithelium-derived cystatin SN enhances eosinophil activation and infiltration through IL-5 in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019 Aug;144(2):455-469. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.03.026. Epub 2019 Apr 8. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30974106 Clinical Trial.
-
Expression of IL-17 and syndecan-1 in nasal polyps and their correlation with nasal polyps.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017 Jun;37(3):412-418. doi: 10.1007/s11596-017-1749-1. Epub 2017 Jun 6. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28585128
-
[Mechanisms underlying glucocorticoid resistance in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Feb 7;53(2):154-160. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2018.02.017. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29429191 Review. Chinese.
-
Research progress of glucocorticoid resistance in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Nov 17;102(46):e36024. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036024. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37986338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
S100a9 might act as a modulator of the Toll-like receptor 4 transduction pathway in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 27;14(1):9722. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60205-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38678138 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatic Vessels in Chronic Rhinosinusitis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Feb 8;17:865-880. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S436450. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38348276 Free PMC article.
-
Colorimetric Aptasensor for the Visual and Microplate Determination of Clusterin in Human Urine Based on Aggregation Characteristics of Gold Nanoparticles.ACS Omega. 2023 Apr 24;8(18):16000-16008. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c08040. eCollection 2023 May 9. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37179603 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal and maternal upregulation of antileukoproteinase in horses.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 26;15:1395030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395030. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38736885 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and Lipidomic Profiles in Nasal Polyps of Glucocorticoid Responders and Non-Responders: Before and After Treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 13;12:814953. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.814953. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35095530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fokkens W. J., Lund V. J., Mullol J., et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. Rhinology. Supplement. 2012;23:1–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

