3D-printed microneedles in biomedical applications
- PMID: 33506186
- PMCID: PMC7814162
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.102012
3D-printed microneedles in biomedical applications
Abstract
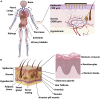
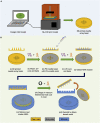
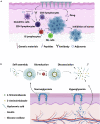
Conventional needle technologies can be advanced with emerging nano- and micro-fabrication methods to fabricate microneedles. Nano-/micro-fabricated microneedles seek to mitigate penetration pain and tissue damage, as well as providing accurately controlled robust channels for administrating bioagents and collecting body fluids. Here, design and 3D printing strategies of microneedles are discussed with emerging applications in biomedical devices and healthcare technologies. 3D printing offers customization, cost-efficiency, a rapid turnaround time between design iterations, and enhanced accessibility. Increasing the printing resolution, the accuracy of the features, and the accessibility of low-cost raw printing materials have empowered 3D printing to be utilized for the fabrication of microneedle platforms. The development of 3D-printed microneedles has enabled the evolution of pain-free controlled release drug delivery systems, devices for extracting fluids from the cutaneous tissue, biosignal acquisition, and point-of-care diagnostic devices in personalized medicine.
Keywords: Biomaterials; Biomedical Materials; Materials in Biotechnology.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures








References
-
- Ali R., Mehta P., Arshad M., Kucuk I., Chang M., Ahmad Z. Transdermal microneedles—a materials perspective. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020;21:12. - PubMed
-
- Amin R., Knowlton S., Hart A., Yenilmez B., Ghaderinezhad F., Katebifar S., Messina M., Khademhosseini A., Tasoglu S. 3D-printed microfluidic devices. Biofabrication. 2016;8:022001. - PubMed
-
- Amin R., Knowlton S., Yenilmez B., Hart A., Joshi A., Tasoglu S. Smart-phone attachable, flow-assisted magnetic focusing device. RSC Adv. 2016;6:93922–93931.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

