Evaluation of Hepatoprotective Activity of Caralluma europaea Stem Extract against CCl4-Induced Hepatic Damage in Wistar Rats
- PMID: 33506211
- PMCID: PMC7810557
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8883040
Evaluation of Hepatoprotective Activity of Caralluma europaea Stem Extract against CCl4-Induced Hepatic Damage in Wistar Rats
Abstract
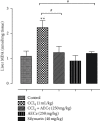
The present study aims to evaluate the hepatoprotective activity of stem aqueous extract of Caralluma europaea (AECe) on carbon tetrachloride- (CCl4-) induced hepatic damage in Wistar rats. The animals were daily treated with the aqueous extract of C. europaea at a dose of 250 mg/kg body weight for 14 days. CCl4 was injected (1 ml/kg, i.p.) two times, on the 7th and 14th days. At the end of the experimental period, all rats were anesthetized to collect blood for the assessment of biochemical parameters and then sacrificed to collect the liver for weighing. Hepatotoxicity was evaluated by measuring the serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bilirubin (total and direct), malondialdehyde (MDA), total protein (TP), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL-c ), low-density lipoprotein (LDL-c), high-density lipoprotein (HDL-c), urea, creatinine, and uric acid. Based on the results obtained in this study, the administration of C. europaea before exposure to the administration of CCl4 conferred favorable hepatoprotective effect in rats. The treatment with AECe (250 mg/kg) exhibits a significant hepatoprotective effect by ameliorating CCl4-induced alterations of these biochemical parameters. Hence, C. europaea could be a potential medicinal herb that can be used in the future to prevent liver intoxication.
Copyright © 2021 Hayat Ouassou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of Fagonia schweinfurthii (Hadidi) Hadidi extract in carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cell line and rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):973-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.048. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24140589
-
Modulatory potentials of the aqueous stem bark extract of Mangifera indica on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.J Tradit Complement Med. 2015 Jan 8;5(2):106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2014.11.001. eCollection 2015 Apr. J Tradit Complement Med. 2015. PMID: 26151020 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Zizyphus lotus L. (Desf.) Fruit against CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Rat.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Dec 25;2019:6161593. doi: 10.1155/2019/6161593. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31949468 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Stachys pilifera ethanol extract in carbon tetrachloride-induce hepatotoxicity in rats.Pharm Biol. 2017 Dec;55(1):1389-1393. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2017.1302484. Pharm Biol. 2017. PMID: 28317417 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient hepatoprotective activity of cranberry extract against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in Wistar albino rat model: Down-regulation of liver enzymes and strong antioxidant activity.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017 Nov;10(11):1054-1058. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017. PMID: 29203101
Cited by
-
Liver-boosting potential: chicory compound-mediated silver nanoparticles for hepatoprotection-biochemical and histopathological insights.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 21;15:1325359. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1325359. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38449804 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective efficacy of quinoa seed extract against CCl4- induced acute liver toxicity in rat model.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Apr 4;12(7):5007-5018. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4149. eCollection 2024 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39055188 Free PMC article.
-
Nephroprotective and Antioxidant Effects of Jatropha dioica Extract Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Wistar Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 21;26(5):1838. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051838. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076464 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Antioxidant Properties, Glucose-Diffusion Effects, α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity, and Antidiabetogenic Effects of C. Europaea Extracts in Experimental Animals.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 31;10(11):1747. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111747. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Mehdar A. A., Dammag M. A., Hussien T. A. Assessment of hepatoprotective activity of Caralluma cicatricosa against CCl4-induced liver damage in rabbits. Journal of Drug Discovery and Therapeutics. 2015;3(34):1–10.
-
- Chen R., Liu J., Chen Z., Cai W.-J., Li X.-F., Lu C.-L. Anthraquinones extract from Morinda angustifolia Roxb. Root alleviates hepatic injury induced by carbon tetrachloride through inhibition of hepatic oxidative stress. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2020;2020 doi: 10.1155/2020/9861571.9861571 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shanmugam G., Ayyavu M., Rao D. M., Devarajan T., Subramaniam G. Hepatoprotective effect of Caralluma umbellate against acetaminophen induced oxidative stress and liver damage in rat. Journal of Pharmacy Research. 2013;6(3):342–345. doi: 10.1016/j.jopr.2013.03.009. - DOI
-
- Subramaniam S., Hedayathullah Khan H. B., Elumalai N., Sudha Lakshmi S. Y. Hepatoprotective effect of ethanolic extract of whole plant of Andrographis paniculata against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Comparative Clinical Pathology. 2015;24(5):1245–1251. doi: 10.1007/s00580-015-2067-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
