NF106: A Neurofibromatosis Clinical Trials Consortium Phase II Trial of the MEK Inhibitor Mirdametinib (PD-0325901) in Adolescents and Adults With NF1-Related Plexiform Neurofibromas
- PMID: 33507822
- PMCID: PMC8078274
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.02220
NF106: A Neurofibromatosis Clinical Trials Consortium Phase II Trial of the MEK Inhibitor Mirdametinib (PD-0325901) in Adolescents and Adults With NF1-Related Plexiform Neurofibromas
Abstract
Purpose: Patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) frequently develop plexiform neurofibromas (PNs), which can cause significant morbidity. We performed a phase II trial of the MAPK/ERK kinase inhibitor, mirdametinib (PD-0325901), in patients with NF1 and inoperable PNs. The primary objective was response rate based on volumetric magnetic resonance imaging analysis.
Methods: Inclusion criteria included age ≥ 16 years and a PN that was either progressive or causing significant morbidity. First-dose pharmacokinetics were performed. Patients completed patient-reported outcome measures. Patients received mirdametinib by mouth twice a day at 2 mg/m2/dose (maximum dose = 4 mg twice a day) in a 3-week on/1-week off sequence. Each course was 4 weeks in duration. Evaluations were performed after four courses for the first year and then after every six courses. Patients could receive a maximum of 24 total courses.
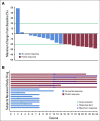
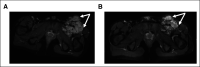
Results: Nineteen patients were enrolled, and all 19 received mirdametinib. The median age was 24 years (range, 16-39 years); the median baseline tumor volume was 363.8 mL (range, 3.9-5,161 mL). Eight of the 19 patients (42%) achieved a partial response of the target PN by course 12, and 10 (53%) had stable disease. One patient (5%) developed progressive disease at course 8. Significant and durable decreases were observed in pain ratings.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this analysis represents the first characterization of the activity and pharmacokinetics of mirdametinib in patients with NF1 and PNs and is the first published response study for MAPK/ERK kinase inhibitors in adults with NF1 and PNs. Mirdametinib given at 2 mg/m2/dose (maximum dose, 4 mg) twice daily in a 3-week on/1-week off sequence resulted in a 42% partial response rate with preliminary evidence of reduction in pain.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02096471.
Figures

References
-
- Monroe CL, Dahiya S, Gutmann DH: Dissecting clinical heterogeneity in neurofibromatosis type 1. Annu Rev Pathol 12:53-74, 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

