Synergistic effect and ultrastructural changes in Trypanosoma cruzi caused by isoobtusilactone A in short exposure of time
- PMID: 33507972
- PMCID: PMC7842926
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245882
Synergistic effect and ultrastructural changes in Trypanosoma cruzi caused by isoobtusilactone A in short exposure of time
Abstract
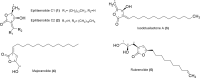
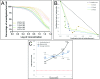
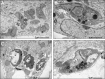
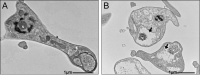
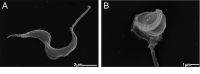
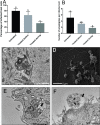
Butanolides have shown a variety of biological effects including anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antiprotozoal effects against certain strains of Trypanosoma cruzi. Considering the lack of an effective drug to treat T. cruzi infections and the prominent results obtained in literature with this class of lactones, we investigated the anti-T. cruzi activity of five butanolides isolated from two species of Lauraceae, Aiouea trinervis and Mezilaurus crassiramea. Initially, the activity of these compounds was evaluated on epimastigote forms of the parasite, after a treatment period of 4 h, followed by testing on amastigotes, trypomastigotes, and mammalian cells. Next, the synergistic effect of active butanolides against amastigotes was evaluated. Further, metacyclogenesis inhibition and infectivity assays were performed for the most active compound, followed by ultrastructural analysis of the treated amastigotes and trypomastigotes. Among the five butanolides studied, majoranolide and isoobtusilactone A were active against all forms of the parasite, with good selectivity indexes in Vero cells. Both butanolides were more active than the control drug against trypomastigote and epimastigote forms and also had a synergic effect on amastigotes. The most active compound, isoobtusilactone A, which showed activity against all tested strains inhibited metacyclogenesis and infection of new host cells. In addition, ultrastructural analysis revealed that this butanolide caused extensive damage to the mitochondria of both amastigotes and trypomastigotes, resulting in severe morphological changes in the infective forms of the parasite. Altogether, our results highlight the potential of butanolides against the etiologic agent of Chagas disease and the relevance of isoobtusilactone A as a strong anti-T. cruzi drug, affecting different events of the life cycle and all evolutionary forms of parasite after a short period of exposure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Sueth-Santiago V, Decote-Ricardo D, Morrot A, Freire-de-Lima CG, Lima MEF. Challenges in the chemotherapy of Chagas disease: looking for possibilities related to the differences and similarities between the parasite and host. World J Biol Chem. 2017;8: 57–80. 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i1.57 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

