Bartonella type IV secretion effector BepC induces stress fiber formation through activation of GEF-H1
- PMID: 33508039
- PMCID: PMC7842913
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009065
Bartonella type IV secretion effector BepC induces stress fiber formation through activation of GEF-H1
Abstract
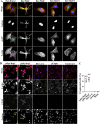
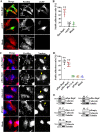
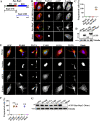
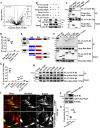
Bartonella T4SS effector BepC was reported to mediate internalization of big Bartonella aggregates into host cells by modulating F-actin polymerization. After that, BepC was indicated to induce host cell fragmentation, an interesting cell phenotype that is characterized by failure of rear-end retraction during cell migration, and subsequent dragging and fragmentation of cells. Here, we found that expression of BepC resulted in significant stress fiber formation and contractile cell morphology, which depended on combination of the N-terminus FIC (filamentation induced by c-AMP) domain and C-terminus BID (Bartonella intracellular delivery) domain of BepC. The FIC domain played a key role in BepC-induced stress fiber formation and cell fragmentation because deletion of FIC signature motif or mutation of two conserved amino acid residues abolished BepC-induced cell fragmentation. Immunoprecipitation confirmed the interaction of BepC with GEF-H1 (a microtubule-associated RhoA guanosine exchange factor), and siRNA-mediated depletion of GEF-H1 prevented BepC-induced stress fiber formation. Interaction with BepC caused the dissociation of GEF-H1 from microtubules and activation of RhoA to induce formation of stress fibers. The ROCK (Rho-associated protein kinase) inhibitor Y27632 completely blocked BepC effects on stress fiber formation and cell contractility. Moreover, stress fiber formation by BepC increased the stability of focal adhesions, which consequently impeded rear-edge detachment. Overall, our study revealed that BepC-induced stress fiber formation was achieved through the GEF-H1/RhoA/ROCK pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bartonella effector protein C mediates actin stress fiber formation via recruitment of GEF-H1 to the plasma membrane.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jan 28;17(1):e1008548. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008548. eCollection 2021 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33508040 Free PMC article.
-
A translocated effector required for Bartonella dissemination from derma to blood safeguards migratory host cells from damage by co-translocated effectors.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jun 19;10(6):e1004187. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004187. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24945914 Free PMC article.
-
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor-H1 regulates cell migration via localized activation of RhoA at the leading edge.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Sep;20(18):4070-82. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-01-0041. Epub 2009 Jul 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19625450 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and functions of the RhoA regulatory guanine nucleotide exchange factor GEF-H1.Small GTPases. 2021 Sep-Nov;12(5-6):358-371. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2020.1840889. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 33126816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Go with the flow: GEF-H1 mediated shear stress mechanotransduction in neutrophils.Small GTPases. 2020 Jan;11(1):23-31. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1332505. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Small GTPases. 2020. PMID: 29188751 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary Diversification of Host-Targeted Bartonella Effectors Proteins Derived from a Conserved FicTA Toxin-Antitoxin Module.Microorganisms. 2021 Jul 31;9(8):1645. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9081645. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34442725 Free PMC article.
-
Anchorage of bacterial effector at plasma membrane via selective phosphatidic acid binding to modulate host cell signaling.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Nov 12;20(11):e1012694. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012694. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39531410 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Bartonella VirB/VirD4 Type IV Secretion System Effectors on Eukaryotic Host Cells.Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 15;12:762582. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.762582. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34975788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

