Predictable cholesterol binding sites in GPCRs lack consensus motifs
- PMID: 33508215
- PMCID: PMC9162085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2021.01.004
Predictable cholesterol binding sites in GPCRs lack consensus motifs
Abstract
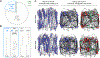
A rich diversity of transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are used by eukaryotes to sense physical and chemical signals. In humans alone, 800 GPCRs comprise the largest and most therapeutically targeted receptor class. Recent advances in GPCR structural biology have produced hundreds of GPCR structures solved by X-ray diffraction and increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). Many of these structures are stabilized by site-specific cholesterol binding, but it is unclear whether these interactions are a product of recurring cholesterol-binding motifs and if observed patterns of cholesterol binding differ by experimental technique. Here, we comprehensively analyze the location and composition of cholesterol binding sites in the current set of 473 human GPCR structural chains. Our findings establish that cholesterol binds similarly in cryo-EM and X-ray structures and show that 92% of cholesterol molecules on GPCR surfaces reside in predictable locations that lack discernable cholesterol-binding motifs.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs); X-ray diffraction; cholesterol; cholesterol consensus motif (CCM); cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) motif; cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM); lipids; structural informatics.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

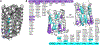

References
-
- Di Scala C, Baier CJ, Evans LS, Williamson PTF, Fantini J, and Barrantes FJ (2017). Relevance of CARC and CRAC cholesterol-recognition motifs in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and other membrane-bound receptors. Curr. Top. Membr. 80, 3–23. - PubMed
-
- Duncan AL, Song W, and Sansom MSP (2020). Lipid-dependent regulation of ion channels and G protein-coupled receptors: insights from structures and simulations. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 60, 31–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

