Maturation, inactivation, and recovery mechanisms of soluble guanylyl cyclase
- PMID: 33508317
- PMCID: PMC7949132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100336
Maturation, inactivation, and recovery mechanisms of soluble guanylyl cyclase
Abstract
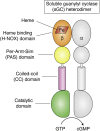
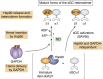
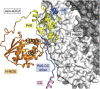
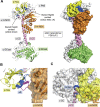
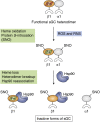
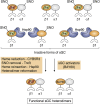
Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) is a heme-containing heterodimeric enzyme that generates many molecules of cGMP in response to its ligand nitric oxide (NO); sGC thereby acts as an amplifier in NO-driven biological signaling cascades. Because sGC helps regulate the cardiovascular, neuronal, and gastrointestinal systems through its cGMP production, boosting sGC activity and preventing or reversing sGC inactivation are important therapeutic and pharmacologic goals. Work over the last two decades is uncovering the processes by which sGC matures to become functional, how sGC is inactivated, and how sGC is rescued from damage. A diverse group of small molecules and proteins have been implicated in these processes, including NO itself, reactive oxygen species, cellular heme, cell chaperone Hsp90, and various redox enzymes as well as pharmacologic sGC agonists. This review highlights their participation and provides an update on the processes that enable sGC maturation, drive its inactivation, or assist in its recovery in various settings within the cell, in hopes of reaching a better understanding of how sGC function is regulated in health and disease.
Keywords: Hsp90; cell signaling; cytochrome b5 reductase; hypertension; nitric oxide; protein nitrosation; protein oxidation.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Garthwaite J. New insight into the functioning of nitric oxide-receptive guanylyl cyclase: Physiological and pharmacological implications. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2010;334:221–232. - PubMed
-
- Pyriochou A., Papapetropoulos A. Soluble guanylyl cyclase: More secrets revealed. Cell Signal. 2005;17:407–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

