Evaluation of chemical compounds that inhibit neurite outgrowth using GFP-labeled iPSC-derived human neurons
- PMID: 33508353
- PMCID: PMC9444042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2021.01.003
Evaluation of chemical compounds that inhibit neurite outgrowth using GFP-labeled iPSC-derived human neurons
Abstract
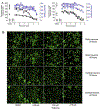
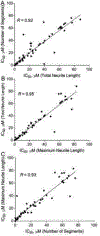
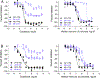
Due to the increasing number of drugs and untested environmental compounds introduced into commercial use, there is recognition for a need to develop reliable and efficient screening methods to identify compounds that may adversely impact the nervous system. One process that has been implicated in neurodevelopment is neurite outgrowth; the disruption of which can result in adverse outcomes that persist later in life. Here, we developed a green fluorescent protein (GFP) labeled neurite outgrowth assay in a high-content, high-throughput format using induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) derived human spinal motor neurons and cortical glutamatergic neurons. The assay was optimized for use in a 1536-well plate format. Then, we used this assay to screen a set of 84 unique compounds that have previously been screened in other neurite outgrowth assays. This library consists of known developmental neurotoxicants, environmental compounds with unknown toxicity, and negative controls. Neurons were cultured for 40 h and then treated with compounds at 11 concentrations ranging from 1.56 nM to 92 μM for 24 and 48 h. Effects of compounds on neurite outgrowth were evaluated by quantifying total neurite length, number of segments, and maximum neurite length per cell. Among the 84 tested compounds, neurite outgrowth in cortical neurons and motor neurons were selectively inhibited by 36 and 31 compounds, respectively. Colchicine, rotenone, and methyl mercuric (II) chloride inhibited neurite outgrowth in both cortical and motor neurons. It is interesting to note that some compounds like parathion and bisphenol AF had inhibitory effects on neurite outgrowth specifically in the cortical neurons, while other compounds, such as 2,2',4,4'-tetrabromodiphenyl ether and caffeine, inhibited neurite outgrowth in motor neurons. The data gathered from these studies show that GFP-labeled iPSC-derived human neurons are a promising tool for identifying and prioritizing compounds with developmental neurotoxicity potential for further hazard characterization.
Keywords: Developmental neurotoxicity; High-content imaging; High-throughput screening; Neurite outgrowth.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Aschner M, Ceccatelli S, Daneshian M, Fritsche E, Hasiwa N, Hartung T, Hogberg HT, Leist M, Li A, Mundi WR, Padilla S, Piersma AH, Bal-Price A, Seiler A, Westerink RH, Zimmer B, Lein PJ, 2017. Reference compounds for alternative test methods to indicate developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) potential of chemicals: example lists and criteria for their selection and use. ALTEX 34(1), 49–74. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bal-Price A, Crofton KM, Leist M, Allen S, Arand M, Buetler T, Delrue N, FitzGerald RE, Hartung T, Heinonen T, Hogberg H, Bennekou SH, Lichtensteiger W, Oggier D, Paparella M, Axelstad M, Piersma A, Rached E, Schilter B, Schmuck G, Stoppini L, Tongiorgi E, Tiramani M, Monnet-Tschudi F, Wilks MF, Ylikomi T, Fritsche E, 2015. International STakeholder NETwork (ISTNET): creating a developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) testing road map for regulatory purposes. Arch Toxicol 89(2), 269–287. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bal-Price A, Hogberg HT, Crofton KM, Daneshian M, FitzGerald RE, Fritsche E, Heinonen T, Bennekou SH, Klima S, Piersma AH, Sachana M, Shafer TJ, Terron A, Monnet-Tschudi F, Viviani B, Waldmann T, Westerink RHS, Wilks MF, Witters H, Zurich MG, Leist M, 2018. Recommendation on Test Readiness Criteria for New Approach Methods in Toxicology: Exemplified for Developmental Neurotoxicity. Altex-Alternatives to Animal Experimentation 35(3), 306–352. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bal-Price AK, Hogberg HT, Buzanska L, Lenas P, van Vliet E, Hartung T, 2010. In vitro developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) testing: relevant models and endpoints. Neurotoxicology 31(5), 545–554. - PubMed
-
- Balmer NV, Weng MK, Zimmer B, Ivanova VN, Chambers SM, Nikolaeva E, Jagtap S, Sachinidis A, Hescheler J, Waldmann T, Leist M, 2012. Epigenetic changes and disturbed neural development in a human embryonic stem cell-based model relating to the fetal valproate syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 21(18), 4104–4114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

