Catching a resurgence: Increase in SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA identified in wastewater 48 h before COVID-19 clinical tests and 96 h before hospitalizations
- PMID: 33508669
- PMCID: PMC7826013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145319
Catching a resurgence: Increase in SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA identified in wastewater 48 h before COVID-19 clinical tests and 96 h before hospitalizations
Abstract
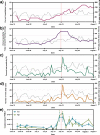
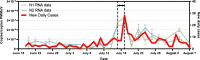
Curtailing the Spring 2020 COVID-19 surge required sweeping and stringent interventions by governments across the world. Wastewater-based COVID-19 epidemiology programs have been initiated in many countries to provide public health agencies with a complementary disease tracking metric and non-discriminating surveillance tool. However, their efficacy in prospectively capturing resurgences following a period of low prevalence is unclear. In this study, the SARS-CoV-2 viral signal was measured in primary clarified sludge harvested every two days at the City of Ottawa's water resource recovery facility during the summer of 2020, when clinical testing recorded daily percent positivity below 1%. In late July, increases of >400% in normalized SARS-CoV-2 RNA signal in wastewater were identified 48 h prior to reported >300% increases in positive cases that were retrospectively attributed to community-acquired infections. During this resurgence period, SARS-CoV-2 RNA signal in wastewater preceded the reported >160% increase in community hospitalizations by approximately 96 h. This study supports wastewater-based COVID-19 surveillance of populations in augmenting the efficacy of diagnostic testing, which can suffer from sampling biases or timely reporting as in the case of hospitalization census.
Keywords: COVID-19; Resurgence; SARS-CoV-2; Virus; Wastewater-based epidemiology; Wave.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that no known competing financial interests or personal relationships could appear to influence the work reported in this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed W., Angel N., Edson J., Bibby K., Bivins A., O’Brien J.W., Choi P.M., Kitajima M., Simpson S.L., Li J., Tscharke B., Verhagen R., Smith W.J.M., Zaugg J., Dierens L., Hugenholtz P., Thomas K.V., Mueller J.F. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;728:138764. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alpaslan-Kocamemi B., Kurt H., Sait A., Sarac F., Saatci A.M., Pakdemirli B. SARS-CoV-2 detection in Istanbul wastewater treatment plant sludges. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.05.12.20099358. 2020.05.12.20099358. - DOI
-
- Bowes D.A., Halden R.U. Theoretical evaluation of using wastewater-based epidemiology to assess the nutritional status of human populations. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Heal. 2019;9:58–63. doi: 10.1016/j.coesh.2019.05.001. - DOI
-
- Bustin S.A., Benes V., Garson J.A., Hellemans J., Huggett J., Kubista M., Mueller R., Nolan T., Pfaffl M.W., Shipley G.L., Vandesompele J., Wittwer C.T. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009;55:611–622. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

