Infrapatellar versus suprapatellar approach for intramedullary nailing of the tibia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33509237
- PMCID: PMC7844899
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-021-02249-0
Infrapatellar versus suprapatellar approach for intramedullary nailing of the tibia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Intramedullary nailing (IMN) is a conventional technique for the treatment of tibial shaft fractures. It has been suggested that the suprapatellar (SP) approach holds advantages over the traditional infrapatellar (IP) approach. Current literature lacks adequate data to provide robust clinical recommendations. This meta-analysis aims to determine the efficacy of infrapatellar versus suprapatellar techniques for IMN.
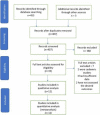
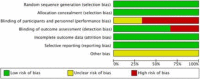
Methods: An up-to-date literature search of the Embase, Medline, and registry platform databases was performed. The search was conducted using a predesigned search strategy and all eligible literature was critically appraised for methodological quality via the Cochrane's collaboration tool. Fluoroscopy time, operative time, pain score, knee function, deep infection, non-union and secondary operation rates were all considered.
Conclusion: A total of twelve studies were included in the meta-analysis. The results of this analysis show that suprapatellar nailing is associated with reduced post-operative pain scores and improved functional outcomes. The data suggest no significant difference in terms of operative times, fluoroscopy times, rates of deep infection, non-union or secondary procedures when compared to infra-patellar techniques. Further studies are required to confirm these findings and assess long-term results.
Keywords: Fixation; Infrapatellar; Suprapatellar; Tibia fracture.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

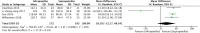
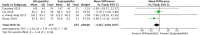
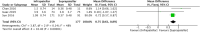


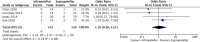
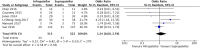
References
-
- Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury. 2006. 10.1016/j.injury.2006.04.130. - PubMed
-
- Bode G, Strohm PC, Südkamp NP, Hammer TO. Tibial shaft fractures - management and treatment options. A review of the current literature. Acta chirurgiae orthopaedicae et traumatologiae Cechoslovaca. 2012;79(6)499–505. - PubMed
-
- Lefaivre KA, Guy P, Chan H, Blachut PA. Long-term follow-up of tibial shaft fractures treated with intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2008. 10.1097/BOT.0b013e318180e646. - PubMed
-
- Väistö O, Toivanen J, Kannus P, Järvinen M. Anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of fractures of the tibial shaft: an eight-year follow-up of a prospective, randomized study comparing two different nail-insertion techniques. J Trauma InjInfect Crit Care. 2008. 10.1097/TA.0b013e318031cd27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

