The loading effect of Pt clusters on Pt/graphene nano sheets catalysts
- PMID: 33510232
- PMCID: PMC7844224
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-80472-1
The loading effect of Pt clusters on Pt/graphene nano sheets catalysts
Abstract
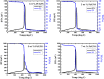
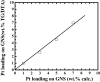
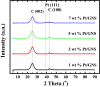
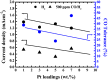
In this paper, we report about chemically interaction between Pt Subnano-Clusters on Graphene Nano Sheets (GNS). The aim of this research is to clarify the size effect of Pt clusters on Pt 1-7 wt.%/GNS. This research is an experimental laboratory research. GNS was synthesized by using modified Hummer's method and 1-7 wt.% Pt/GNS were prepared with impregnation method. Then, they were analyzed with TG/DTA, XRD, TEM and XPS, respectively. The results show that Pt clusters are well deposited on GNS (TG/DTA and TEM data). Those data also are consistent with XRD data. The weak and broad peaks appear at 2θ = 39°, indicating Pt metal exists on GNS. The state of Pt is confirmed by using XPS. The appearance of Pt 4f. peaks proves that Pt metal is chemical interaction on GNS. The size of Pt clusters may affect the chemically properties of Pt/GNS catalysts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






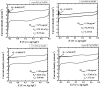
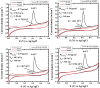
References
-
- Siburian R, Nakamura J. Formation process of Pt subnano-clusters on graphene nanosheets. J Phys Chem C. 2012;116:22947–22953. doi: 10.1021/jp307327e. - DOI
-
- Siburian R, Kondo T, Nakamura J. Size control to a sub-nanometer scale in platinum catalysts on graphene. J Phys Chem C. 2013;117:3635–3645. doi: 10.1021/jp311852j. - DOI
-
- Siburian R, Sebayang K, Supeno M, Marpaung H. Effect of platinum loading on graphene nano sheets at cathode. Orient. J. Chem. 2017;33:134–140. doi: 10.13005/ojc/330114. - DOI
-
- Shi H, Auerbach SM, Ramasubramaniam A. First-principles predictions of structure-function relationships of graphene-supported platinum nanoclusters. J. Phys. Chem. 2016;120:11899–11909. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b01288. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

