Oral absorption and drug interaction kinetics of moxifloxacin in an animal model of weightlessness
- PMID: 33510326
- PMCID: PMC7843972
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-82044-3
Oral absorption and drug interaction kinetics of moxifloxacin in an animal model of weightlessness
Abstract
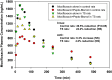
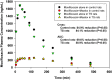
To investigate the effect of simulated weightlessness on the pharmacokinetics of orally administered moxifloxacin and the antacid Maalox or the antidiarrheal Pepto-Bismol using a tail-suspended (TS) rat model of microgravity. Fasted control and TS, jugular-vein-cannulated, male Sprague-Dawley rats received either a single 5 mg/kg intravenous dose or a single 10 mg/kg oral dose of moxifloxacin alone or with a 0.625 mL/kg oral dose of Maalox or a 1.43 mL/kg oral dose of Pepto-Bismol. Plasma concentrations of moxifloxacin were measured by HPLC. Pharmacokinetic data were analyzed using WinNonlin. Simulated weightlessness had no effect on moxifloxacin disposition after intravenous administration but significantly decreased the extent of moxifloxacin oral absorption. The coadministration of moxifloxacin with Maalox to either control or TS rats caused significant reductions in the rate and extent of moxifloxacin absorption. In contrast, the coadministration of moxifloxacin with Pepto-Bismol to TS rats had no significant effect on either the rate or the extent of moxifloxacin absorption. These interactions showed dose staggering when oral administrations of Pepto-Bismol and moxifloxacin were separated by 60 min in control rats but not in TS rats. Dose staggering was more apparent after the coadministration of Maalox and moxifloxacin in TS rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of pharmacokinetic interaction between the oral anti-influenza neuraminidase inhibitor prodrug oseltamivir and antacids.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002 Oct;54(4):372-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2002.01678.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12392584 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of the influence of antacids and H2 antagonists on the absorption of moxifloxacin after oral administration of a 400mg dose to healthy volunteers.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001;40 Suppl 1:39-48. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200140001-00006. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2001. PMID: 11352441 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative absorption of bismuth in Sprague-Dawley rats following oral administration of preparations containing bismuth sucrose octasulfate, bismuth subsalicylate, and bismuth subcitrate.Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1997 Jan;18(1):1-8. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-081x(199701)18:1<1::aid-bdd996>3.0.co;2-0. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1997. PMID: 9008264
-
Lack of interaction between valaciclovir, the L-valyl ester of acyclovir, and Maalox antacid.J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996 Feb;37(2):383-7. doi: 10.1093/jac/37.2.383. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996. PMID: 8707752 Clinical Trial.
-
Bismuth subsalicylate: history, chemistry, and safety.Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12 Suppl 1:S3-8. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.supplement_1.s3. Rev Infect Dis. 1990. PMID: 2406853 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Dexketoprofen on the Disposition Kinetics of Moxifloxacin in Plasma and Lung in Male and Female Rats.Curr Drug Metab. 2024;25(1):63-70. doi: 10.2174/0113892002282271231219044508. Curr Drug Metab. 2024. PMID: 38258775
-
Alteration of Gastrointestinal Function and the Ameliorative Effects of Hericium erinaceus Polysaccharides in Tail Suspension Rats.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 18;17(4):724. doi: 10.3390/nu17040724. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40005052 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal Adhesive Chitosan Nanogel Formulations of Antibiotics and Adjuvants (Terpenoids, Flavonoids, etc.) and Their Potential for the Treatment of Infectious Diseases of the Gastrointestinal Tract.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 20;15(9):2353. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092353. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Putcha L, Berens KL, Marshburn TH, Ortega HJ, Billica RD. Pharmaceutical use by U.S. astronauts on space shuttle missions. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1999;70:705–708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

