The chromosome-level reference genome assembly for Panax notoginseng and insights into ginsenoside biosynthesis
- PMID: 33511345
- PMCID: PMC7816079
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xplc.2020.100113
The chromosome-level reference genome assembly for Panax notoginseng and insights into ginsenoside biosynthesis
Abstract
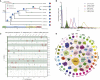
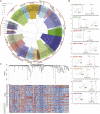
Panax notoginseng, a perennial herb of the genus Panax in the family Araliaceae, has played an important role in clinical treatment in China for thousands of years because of its extensive pharmacological effects. Here, we report a high-quality reference genome of P. notoginseng, with a genome size up to 2.66 Gb and a contig N50 of 1.12 Mb, produced with third-generation PacBio sequencing technology. This is the first chromosome-level genome assembly for the genus Panax. Through genome evolution analysis, we explored phylogenetic and whole-genome duplication events and examined their impact on saponin biosynthesis. We performed a detailed transcriptional analysis of P. notoginseng and explored gene-level mechanisms that regulate the formation of characteristic tubercles. Next, we studied the biosynthesis and regulation of saponins at temporal and spatial levels. We combined multi-omics data to identify genes that encode key enzymes in the P. notoginseng terpenoid biosynthetic pathway. Finally, we identified five glycosyltransferase genes whose products catalyzed the formation of different ginsenosides in P. notoginseng. The genetic information obtained in this study provides a resource for further exploration of the growth characteristics, cultivation, breeding, and saponin biosynthesis of P. notoginseng.
Keywords: P. notoginseng; chromosome-level; genome; ginsenoside; regulation; transcriptome.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SMRT- and Illumina-based RNA-seq analyses unveil the ginsinoside biosynthesis and transcriptomic complexity in Panax notoginseng.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 17;10(1):15310. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72291-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32943706 Free PMC article.
-
The Medicinal Herb Panax notoginseng Genome Provides Insights into Ginsenoside Biosynthesis and Genome Evolution.Mol Plant. 2017 Jun 5;10(6):903-907. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2017.02.011. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Mol Plant. 2017. PMID: 28315473 No abstract available.
-
Transcriptome analysis of leaves, roots and flowers of Panax notoginseng identifies genes involved in ginsenoside and alkaloid biosynthesis.BMC Genomics. 2015 Apr 3;16(1):265. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1477-5. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25886736 Free PMC article.
-
[Overview of research in ginsenosides glycosyltransferase].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Oct;45(19):4574-4581. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200508.602. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33164420 Review. Chinese.
-
Panax notoginseng: panoramagram of phytochemical and pharmacological properties, biosynthesis, and regulation and production of ginsenosides.Hortic Res. 2024 Jul 2;11(8):uhae170. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae170. eCollection 2024 Aug. Hortic Res. 2024. PMID: 39135729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomics and metabolomics revealed the molecular basis of the color formation in the roots of Panax notoginseng.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 10;10(18):e37532. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37532. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39381219 Free PMC article.
-
A reference-grade genome assembly for Astragalus mongholicus and insights into the biosynthesis and high accumulation of triterpenoids and flavonoids in its roots.Plant Commun. 2023 Mar 13;4(2):100469. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2022.100469. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Plant Commun. 2023. PMID: 36307985 Free PMC article.
-
De novo and comparative transcriptomic analysis explain morphological differences in Panax notoginseng taproots.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jan 31;23(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08283-w. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35100996 Free PMC article.
-
The chromosome-level reference genome assembly for Dendrobium officinale and its utility of functional genomics research and molecular breeding study.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Jul;11(7):2080-2092. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.01.019. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34386340 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of morphogenesis and metabolism by plant cell biomechanics: from model plants to traditional herbs.Hortic Res. 2025 Jan 16;12(4):uhaf011. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhaf011. eCollection 2025 Apr. Hortic Res. 2025. PMID: 40093376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan P., Thomas G., Tomlinson B. Protective effects of trilinolein extracted from Panax notoginseng against cardiovascular disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2002;23:1157–1162. - PubMed
-
- Chen W., Kui L., Zhang G., Zhu S., Zhang J., Wang X., Yang M., Huang H., Liu Y., Wang Y. Whole-genome sequencing and analysis of the Chinese herbal plant Panax notoginseng. Mol. Plant. 2017;10:899–902. - PubMed
-
- Collu G., Unver N., Peltenburg-Looman M.G.A., Heijden R.v.d., Verpoorte R., Memelink J. Geraniol 10-hydroxylase, a cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis. Fed. Eur. Biochem. Soc. 2001;508:215–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

