Therapeutic inhibition of HIF-2α reverses polycythemia and pulmonary hypertension in murine models of human diseases
- PMID: 33512384
- PMCID: PMC8109019
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020009138
Therapeutic inhibition of HIF-2α reverses polycythemia and pulmonary hypertension in murine models of human diseases
Abstract
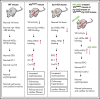
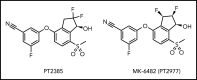
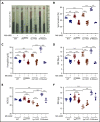
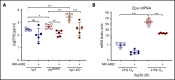
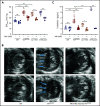
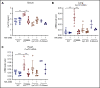
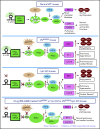
Polycythemia and pulmonary hypertension are 2 human diseases for which better therapies are needed. Upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α (HIF-2α) and its target genes, erythropoietin (EPO) and endothelin-1, causes polycythemia and pulmonary hypertension in patients with Chuvash polycythemia who are homozygous for the R200W mutation in the von Hippel Lindau (VHL) gene and in a murine mouse model of Chuvash polycythemia that bears the same homozygous VhlR200W mutation. Moreover, the aged VhlR200W mice developed pulmonary fibrosis, most likely due to the increased expression of Cxcl-12, another Hif-2α target. Patients with mutations in iron regulatory protein 1 (IRP1) also develop polycythemia, and Irp1-knockout (Irp1-KO) mice exhibit polycythemia, pulmonary hypertension, and cardiac fibrosis attributable to translational derepression of Hif-2α, and the resultant high expression of the Hif-2α targets EPO, endothelin-1, and Cxcl-12. In this study, we inactivated Hif-2α with the second-generation allosteric HIF-2α inhibitor MK-6482 in VhlR200W, Irp1-KO, and double-mutant VhlR200W;Irp1-KO mice. MK-6482 treatment decreased EPO production and reversed polycythemia in all 3 mouse models. Drug treatment also decreased right ventricular pressure and mitigated pulmonary hypertension in VhlR200W, Irp1-KO, and VhlR200W;Irp1-KO mice to near normal wild-type levels and normalized the movement of the cardiac interventricular septum in VhlR200Wmice. MK-6482 treatment reduced the increased expression of Cxcl-12, which, in association with CXCR4, mediates fibrocyte influx into the lungs, potentially causing pulmonary fibrosis. Our results suggest that oral intake of MK-6482 could represent a new approach to treatment of patients with polycythemia, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis, and complications caused by elevated expression of HIF-2α.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
HIF-2 inhibitor, erythrocytosis, and pulmonary hypertension.Blood. 2021 May 6;137(18):2424-2425. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020010323. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33956067 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bento C. Genetic basis of congenital erythrocytosis. Int J Lab Hematol. 2018;40(suppl 1):62-67. - PubMed
-
- Oliveira JL, Coon LM, Frederick LA, et al. . Genotype-Phenotype Correlation of Hereditary Erythrocytosis Mutations, a single center experience. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(8):1029-1041. - PubMed
-
- Semenza GL. The Genomics and Genetics of Oxygen Homeostasis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2020;21(1):183-204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

