Stanniocalcin 1 is a phagocytosis checkpoint driving tumor immune resistance
- PMID: 33513345
- PMCID: PMC8044011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.12.023
Stanniocalcin 1 is a phagocytosis checkpoint driving tumor immune resistance
Abstract
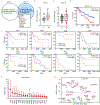
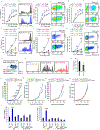
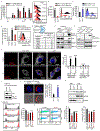
Immunotherapy induces durable clinical responses in a fraction of patients with cancer. However, therapeutic resistance poses a major challenge to current immunotherapies. Here, we identify that expression of tumor stanniocalcin 1 (STC1) correlates with immunotherapy efficacy and is negatively associated with patient survival across diverse cancer types. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments demonstrate that tumor STC1 supports tumor progression and enables tumor resistance to checkpoint blockade in murine tumor models. Mechanistically, tumor STC1 interacts with calreticulin (CRT), an "eat-me" signal, and minimizes CRT membrane exposure, thereby abrogating membrane CRT-directed phagocytosis by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), including macrophages and dendritic cells. Consequently, this impairs APC capacity of antigen presentation and T cell activation. Thus, tumor STC1 inhibits APC phagocytosis and contributes to tumor immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance. We suggest that STC1 is a previously unappreciated phagocytosis checkpoint and targeting STC1 and its interaction with CRT may sensitize to cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: PD-1; T cell immunity; calreticulin; checkpoint; dendritic cell; eat-me signal; macrophages; phagocytosis; stanniocalcin 1; tumor.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Subversion of calreticulin exposure as a strategy of immune escape.Cancer Cell. 2021 Apr 12;39(4):449-451. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.01.014. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Cancer Cell. 2021. PMID: 33513346
References
-
- Chan KK, Leung CO, Wong CC, Ho DW, Chok KS, Lai CL, Ng IO, and Lo RC (2017). Secretory Stanniocalcin 1 promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through activation of JNK signaling pathway. Cancer Lett 403, 330–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

