Effective Locations for Injecting Botulinum Toxin into the Mentalis Muscle; Cadaveric and Ultrasonographic Study
- PMID: 33514053
- PMCID: PMC7911364
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins13020096
Effective Locations for Injecting Botulinum Toxin into the Mentalis Muscle; Cadaveric and Ultrasonographic Study
Abstract
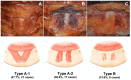
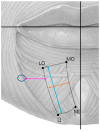
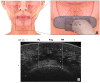
The mentalis muscle is now considered key structures when performing procedures for rejuvenating the lower face. The aim of this study was to determine the anatomical morphology and location of the mentalis muscle and thereby provide anatomical information for facilitating clinical procedures designed to rejuvenate the lower face. Forty-four adult hemifaces from five Thai cadavers and 21 Korean cadavers were dissected to identify the locations of the mentalis muscle. Sixty-six hemifaces from 33 healthy young Korean subjects were included in an ultrasonographic study. The depth of the mentalis muscle below the skin surface, the thickness of the mentalis muscle, and the distance from the bone to the mentalis muscle were measured at the two points that were 5 mm lateral to the most-prominent point of the chin. The mentalis muscle was classified into two types based to its shape: in type A (86.4%, 38 of the 44 cases) it was dome shaped in three dimensions, while in type B (13.6%, 6 of the 44 cases) it was flat. The mentalis muscle was present mostly at the area 5-10 mm from the midsagittal line and 20-30 mm from a horizontal line connecting the mouth corners. The mentalis muscle was present between depths of 6.7 to 10.7 mm below the skin. This new information about the location of the mentalis muscle may help when identifying the most effective and safe botulinum toxin injection points and depths during esthetic procedures for weakened facial rhytides on the lower face.
Keywords: botulinum toxin; facial rejuvenating; facial rhytides; injection procedure; mental crease; mentalis muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Kim H.-J., Seo K.K., Lee H.-K., Kim J. Clinical Anatomy of the Face for Filler and Botulinum Toxin Injection. Springer; Singapore: 2016. General Anatomy of the Face and Neck; pp. 1–53.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

