Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 pseudovirus by BNT162b2 vaccine-elicited human sera
- PMID: 33514629
- PMCID: PMC7971771
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abg6105
Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 pseudovirus by BNT162b2 vaccine-elicited human sera
Abstract
Recently, a new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) lineage called B.1.1.7 (variant of concern: VOC 202012/01), which is reported to spread more efficiently and faster than other strains, emerged in the United Kingdom. This variant has an unusually large number of mutations, with 10 amino acid changes in the spike (S) protein, raising concerns that its recognition by neutralizing antibodies may be affected. In this study, we tested SARS-CoV-2-S pseudoviruses bearing either the Wuhan reference strain or the B.1.1.7 lineage spike protein with sera of 40 participants who were vaccinated in a previously reported trial with the messenger RNA-based COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b2. The immune sera had slightly reduced but overall largely preserved neutralizing titers against the B.1.1.7 lineage pseudovirus. These data indicate that the B.1.1.7 lineage will not escape BNT162b2-mediated protection.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
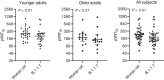
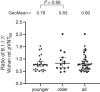
Comment in
-
Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern.Science. 2021 Mar 12;371(6534):1103-1104. doi: 10.1126/science.abg7404. Science. 2021. PMID: 33707254 No abstract available.
References
-
- Polack F. P., Thomas S. J., Kitchin N., Absalon J., Gurtman A., Lockhart S., Perez J. L., Pérez Marc G., Moreira E. D., Zerbini C., Bailey R., Swanson K. A., Roychoudhury S., Koury K., Li P., Kalina W. V., Cooper D., Frenck R. W. Jr.., Hammitt L. L., Türeci Ö., Nell H., Schaefer A., Ünal S., Tresnan D. B., Mather S., Dormitzer P. R., Şahin U., Jansen K. U., Gruber W. C.; C4591001 Clinical Trial Group , Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 2603–2615 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2034577 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- A. Rambaut, N. Loman, O. Pybus, W. Barclay, J. Barrett, A. Carabelli, T. Connor, T. Peacock, D. L. Robertson, E. Volz; COVID-19 Genomics Consortium UK (CoG-UK), Preliminary genomic characterisation of an emergent SARS-CoV-2 lineage in the UK defined by a novel set of spike mutations. virological.org (2020); https://virological.org/t/preliminary-genomic-characterisation-of-an-eme....
-
- E. Volz, S. Mishra, M. Chand, J. C. Barrett, R. Johnson, L. Geidelberg, W. R. Hinsley, D. J. Laydon, G. Dabrera, Á. O’Toole, R. Amato, M. Ragonnet-Cronin, I. Harrison, B. Jackson, C. V. Ariani, O. Boyd, N. J. Loman, J. T. McCrone, S. Gonçalves, D. Jorgensen, R. Myers, V. Hill, D. K. Jackson, K. Gaythorpe, N. Groves, J. Sillitoe, D. P. Kwiatkowski, The COVID-19 Genomics UK (COG-UK) consortium, S. Flaxman, O. Ratmann, S. Bhatt, S. Hopkins, A. Gandy, A. Rambaut, N. M. Ferguson, Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Lineage B.1.1.7 in England: Insights from linking epidemiological and genetic data. medRxiv 2020.12.30.20249034 [Preprint]. 4 January 2021. 10.1101/2020.12.30.20249034.10.1101/2020.12.30.20249034 - DOI - DOI
-
- Starr T. N., Greaney A. J., Hilton S. K., Ellis D., Crawford K. H. D., Dingens A. S., Navarro M. J., Bowen J. E., Tortorici M. A., Walls A. C., King N. P., Veesler D., Bloom J. D., Deep Mutational Scanning of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Reveals Constraints on Folding and ACE2 Binding. Cell 182, 1295–1310.e20 (2020). 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gu H., Chen Q., Yang G., He L., Fan H., Deng Y. Q., Wang Y., Teng Y., Zhao Z., Cui Y., Li Y., Li X. F., Li J., Zhang N. N., Yang X., Chen S., Guo Y., Zhao G., Wang X., Luo D. Y., Wang H., Yang X., Li Y., Han G., He Y., Zhou X., Geng S., Sheng X., Jiang S., Sun S., Qin C. F., Zhou Y., Adaptation of SARS-CoV-2 in BALB/c mice for testing vaccine efficacy. Science 369, 1603–1607 (2020). 10.1126/science.abc4730 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

