Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions
- PMID: 33514693
- PMCID: PMC7846842
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-020-00125-x
Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions
Abstract
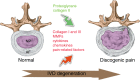
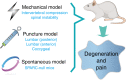
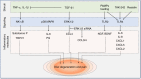
Low back pain (LBP), as a leading cause of disability, is a common musculoskeletal disorder that results in major social and economic burdens. Recent research has identified inflammation and related signaling pathways as important factors in the onset and progression of disc degeneration, a significant contributor to LBP. Inflammatory mediators also play an indispensable role in discogenic LBP. The suppression of LBP is a primary goal of clinical practice but has not received enough attention in disc research studies. Here, an overview of the advances in inflammation-related pain in disc degeneration is provided, with a discussion on the role of inflammation in IVD degeneration and pain induction. Puncture models, mechanical models, and spontaneous models as the main animal models to study painful disc degeneration are discussed, and the underlying signaling pathways are summarized. Furthermore, potential drug candidates, either under laboratory investigation or undergoing clinical trials, to suppress discogenic LBP by eliminating inflammation are explored. We hope to attract more research interest to address inflammation and pain in IDD and contribute to promoting more translational research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 81371984/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81902204/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81772386/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- R01 AR078857/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 81572175/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

