PDX1LOW MAFALOW β-cells contribute to islet function and insulin release
- PMID: 33514698
- PMCID: PMC7846747
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20632-z
PDX1LOW MAFALOW β-cells contribute to islet function and insulin release
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: PDX1LOW MAFALOW β-cells contribute to islet function and insulin release.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 20;12(1):4521. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24848-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34285239 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
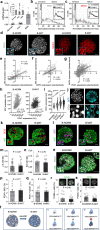
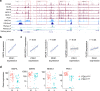
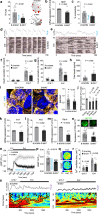
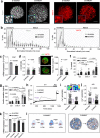
Transcriptionally mature and immature β-cells co-exist within the adult islet. How such diversity contributes to insulin release remains poorly understood. Here we show that subtle differences in β-cell maturity, defined using PDX1 and MAFA expression, contribute to islet operation. Functional mapping of rodent and human islets containing proportionally more PDX1HIGH and MAFAHIGH β-cells reveals defects in metabolism, ionic fluxes and insulin secretion. At the transcriptomic level, the presence of increased numbers of PDX1HIGH and MAFAHIGH β-cells leads to dysregulation of gene pathways involved in metabolic processes. Using a chemogenetic disruption strategy, differences in PDX1 and MAFA expression are shown to depend on islet Ca2+ signaling patterns. During metabolic stress, islet function can be restored by redressing the balance between PDX1 and MAFA levels across the β-cell population. Thus, preserving heterogeneity in PDX1 and MAFA expression, and more widely in β-cell maturity, might be important for the maintenance of islet function.
Conflict of interest statement
G.A.R. has received grant funding from Servier and is a consultant for Sun Pharma. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


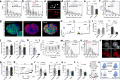

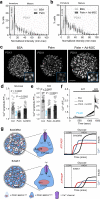
References
-
- Rutter GA, Pullen TJ, Hodson DJ, Martinez-Sanchez A. Pancreatic beta-cell identity, glucose sensing and the control of insulin secretion. Biochem. J. 2015;466:203–218. - PubMed
-
- Frank JA, et al. Optical tools for understanding the complexity of β-cell signalling and insulin release. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018;14:721–737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

