Single-cell transcriptomics following ischemic injury identifies a role for B2M in cardiac repair
- PMID: 33514846
- PMCID: PMC7846780
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-01636-3
Single-cell transcriptomics following ischemic injury identifies a role for B2M in cardiac repair
Abstract
The efficiency of the repair process following ischemic cardiac injury is a crucial determinant for the progression into heart failure and is controlled by both intra- and intercellular signaling within the heart. An enhanced understanding of this complex interplay will enable better exploitation of these mechanisms for therapeutic use. We used single-cell transcriptomics to collect gene expression data of all main cardiac cell types at different time-points after ischemic injury. These data unveiled cellular and transcriptional heterogeneity and changes in cellular function during cardiac remodeling. Furthermore, we established potential intercellular communication networks after ischemic injury. Follow up experiments confirmed that cardiomyocytes express and secrete elevated levels of beta-2 microglobulin in response to ischemic damage, which can activate fibroblasts in a paracrine manner. Collectively, our data indicate phase-specific changes in cellular heterogeneity during different stages of cardiac remodeling and allow for the identification of therapeutic targets relevant for cardiac repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


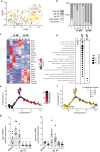
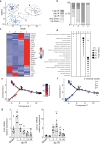
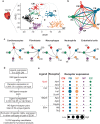
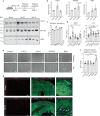
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

