Patient-tailored antithrombotic therapy following percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 33515031
- PMCID: PMC8244639
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1097
Patient-tailored antithrombotic therapy following percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
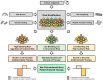
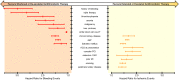
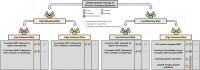
Dual antiplatelet therapy has long been the standard of care in preventing coronary and cerebrovascular thrombotic events in patients with chronic coronary syndrome and acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, but choosing the optimal treatment duration and composition has become a major challenge. Numerous studies have shown that certain patients benefit from either shortened or extended treatment duration. Furthermore, trials evaluating novel antithrombotic strategies, such as P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy, low-dose factor Xa inhibitors on top of antiplatelet therapy, and platelet function- or genotype-guided (de-)escalation of treatment, have shown promising results. Current guidelines recommend risk stratification for tailoring treatment duration and composition. Although several risk stratification methods evaluating ischaemic and bleeding risk are available to clinicians, such as the use of risk scores, platelet function testing , and genotyping, risk stratification has not been broadly adopted in clinical practice. Multiple risk scores have been developed to determine the optimal treatment duration, but external validation studies have yielded conflicting results in terms of calibration and discrimination and there is limited evidence that their adoption improves clinical outcomes. Likewise, platelet function testing and genotyping can provide useful prognostic insights, but trials evaluating treatment strategies guided by these stratification methods have produced mixed results. This review critically appraises the currently available antithrombotic strategies and provides a viewpoint on the use of different risk stratification methods alongside clinical judgement in current clinical practice.
Keywords: Patient-tailored antithrombotic therapy; Risk stratification; Dual antiplatelet therapy.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

References
-
- Valgimigli M, Bueno H, Byrne RA, Collet J-P, Costa F, Jeppsson A, Jüni P, Kastrati A, Kolh P, Mauri L, Montalescot G, Neumann F-J, Petricevic M, Roffi M, Steg PG, Windecker S, Zamorano JL, Levine GN, Badimon L, Vranckx P, Agewall S, Andreotti F, Antman E, Barbato E, Bassand J-P, Bugiardini R, Cikirikcioglu M, Cuisset T, De Bonis M, Delgado V, Fitzsimons D, Gaemperli O, Galiè N, Gilard M, Hamm CW, Ibanez B, Iung B, James S, Knuuti J, Landmesser U, Leclercq C, Lettino M, Lip G, Piepoli MF, Pierard L, Schwerzmann M, Sechtem U, Simpson IA, Uva MS, Stabile E, Storey RF, Tendera M, Van de Werf F, Verheugt F, Aboyans V, Windecker S, Aboyans V, Agewall S, Barbato E, Bueno H, Coca A, Collet J-P, Coman IM, Dean V, Delgado V, Fitzsimons D, Gaemperli O, Hindricks G, Iung B, Jüni P, Katus HA, Knuuti J, Lancellotti P, Leclercq C, McDonagh T, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Richter DJ, Roffi M, Shlyakhto E, Simpson IA, Zamorano JL, Windecker S, Aboyans V, Agewall S, Barbato E, Bueno H, Coca A, Collet J-P, Coman IM, Dean V, Delgado V, Fitzsimons D, Gaemperli O, Hindricks G, Iung B, Jüni P, Katus HA, Knuuti J, Lancellotti P, Leclercq C, McDonagh T, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Richter DJ, Roffi M, Shlyakhto E, Simpson IA, Zamorano JL, Roithinger FX, Aliyev F, Stelmashok V, Desmet W, Postadzhiyan A, Georghiou GP, Motovska Z, Grove EL, Marandi T, Kiviniemi T, Kedev S, Gilard M, Massberg S, Alexopoulos D, Kiss RG, Gudmundsdottir IJ, McFadden EP, Lev E, De Luca L, Sugraliyev A, Haliti E, Mirrakhimov E, Latkovskis G, Petrauskiene B, Huijnen S, Magri CJ, Cherradi R, Ten Berg JM, Eritsland J, Budaj A, Aguiar CT, Duplyakov D, Zavatta M, Antonijevic NM, Motovska Z, Fras Z, Montoliu AT, Varenhorst C, Tsakiris D, Addad F, Aydogdu S, Parkhomenko A, Kinnaird T; Group ESD, Guidelines ECfP, Societies ENC. 2017 ESC focused update on dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease developed in collaboration with EACTS: the Task Force for dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J 2018;39:213–260. - PubMed
-
- Levine GN, Bates ER, Bittl JA, Brindis RG, Fihn SD, Fleisher LA, Granger CB, Lange RA, Mack MJ, Mauri L, Mehran R, Mukherjee D, Newby LK, O’Gara PT, Sabatine MS, Smith PK, Smith SC. Jr. 2016 ACC/AHA Guideline focused update on duration of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with coronary artery disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;68:1082–1115. - PubMed
-
- Collet J-P, Thiele H, Barbato E, Barthélémy O, Bauersachs J, Bhatt DL, Dendale P, Dorobantu M, Edvardsen T, Folliguet T, Gale CP, Gilard M, Jobs A, Jüni P, Lambrinou E, Lewis BS, Mehilli J, Meliga E, Merkely B, Mueller C, Roffi M, Rutten FH, Sibbing D, Siontis GCM; Group ESD. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: the Task Force for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2020;doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa575. - PubMed
-
- Sharma A, Hagstrom E, Wojdyla DM, Neely ML, Harrington RA, Wallentin L, Alexander JH, Goodman SG, Lopes RD. Clinical consequences of bleeding among individuals with a recent acute coronary syndrome: insights from the APPRAISE-2 trial. Am Heart J 2019;215:106–113. - PubMed
-
- Tada T, Byrne RA, Simunovic I, King LA, Cassese S, Joner M, Fusaro M, Schneider S, Schulz S, Ibrahim T, Ott I, Massberg S, Laugwitz KL, Kastrati A. Risk of stent thrombosis among bare-metal stents, first-generation drug-eluting stents, and second-generation drug-eluting stents: results from a registry of 18,334 patients. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2013;6:1267–1274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

