Pulmonary venous thrombosis in a patient with COVID-19 infection
- PMID: 33515360
- PMCID: PMC7846916
- DOI: 10.1007/s11239-021-02388-5
Pulmonary venous thrombosis in a patient with COVID-19 infection
Abstract
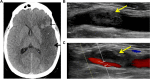
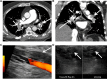
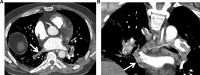
Objectives: Infection with the SARS-COV2 virus (COVID-19) may be complicated by thrombotic diathesis. This complication often involves the pulmonary microcirculation. While macrovascular thrombotic complications of the lung may include pulmonary artery embolism, pulmonary artery thrombus in situ has also been hypothesized. Pulmonary vein thrombosis has not been described in this context.
Methods/results: Herein, we provide a case of an otherwise healthy male who developed an ischemic stroke with left internal carotid thrombus. Further imaging revealed pulmonary emboli with propagation through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium. This left atrial thrombus provides a source of atypical "paradoxic arterial embolism".
Conclusions: Thrombotic outcomes in the setting of severe COVID 19 pneumonia may include macrovascular venous thromboembolism, microvascular pulmonary vascular thrombosis and arterial thromboembolism. Pulmonary vein, herein described, provides further mechanistic pathway for potential arterial embolic phenomenon.
Keywords: COVID-19; Pulmonary vein thrombosis; Stroke; Venous thromboembolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perspective: The Case for Acute Large Vessel Ischemic Stroke in COVID-19 Originating Within Thrombosed Pulmonary Venules.Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):2411-2419. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.038056. Epub 2022 May 11. Stroke. 2022. PMID: 35543127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aortic thrombus in patients with severe COVID-19: review of three cases.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021 Jan;51(1):237-242. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02219-z. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021. PMID: 32648092 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptogenic, Embolic Stroke-Looking Backstage.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022 May;31(5):106353. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106353. Epub 2022 Mar 2. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022. PMID: 35247732
-
Venous thromboembolism and COVID-19: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2020 Oct 15;14(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13256-020-02516-4. J Med Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33054805 Free PMC article.
-
Very late unusual thrombosis of the remnant pulmonary vasculatures after lung resection complicated by embolic events.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019 Nov 12;14(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s13019-019-1013-9. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31718656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acute COVID-19 Pneumonia Unmasking a Large Left Atrial Myxoma.Int J Angiol. 2022 Aug 25;32(4):280-283. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1756203. eCollection 2023 Dec. Int J Angiol. 2022. PMID: 37927831 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective: The Case for Acute Large Vessel Ischemic Stroke in COVID-19 Originating Within Thrombosed Pulmonary Venules.Stroke. 2022 Jul;53(7):2411-2419. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.038056. Epub 2022 May 11. Stroke. 2022. PMID: 35543127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombosis of the vasa vasorum of the large and medium size pulmonary artery and vein leads to pulmonary thromboembolism in COVID-19.Autops Case Rep. 2024 May 22;14:e2024491. doi: 10.4322/acr.2024.491. eCollection 2024. Autops Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38803482 Free PMC article.
-
The COVID-19 thrombus: distinguishing pathological, mechanistic, and phenotypic features and management.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025 Jan;58(1):15-49. doi: 10.1007/s11239-024-03028-4. Epub 2024 Aug 23. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025. PMID: 39179952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary vein thrombosis: Clinical presentation and outcomes.Thromb Res. 2024 Jul;239:109028. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2024.05.001. Epub 2024 May 10. Thromb Res. 2024. PMID: 38735167 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

