[Role of the French national registry REIN in the health monitoring of patients with end-stage chronic renal failure infected with SARS-CoV-2: Organization and initial data]
- PMID: 33516618
- PMCID: PMC7792522
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nephro.2020.11.005
[Role of the French national registry REIN in the health monitoring of patients with end-stage chronic renal failure infected with SARS-CoV-2: Organization and initial data]
Abstract
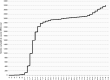
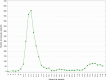
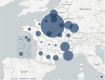
The REIN registry is a national registry held by the French Biomedicine Agency. Its objective is the epidemiological monitoring of patients with end-stage chronic renal failure. This registry, backed by its expertise and its national network, has been able to very quickly set up epidemiological monitoring of chronic dialysis and/or transplant patients affected by SARS-CoV-2. The first results show a relatively low frequency of COVID-19 in dialysis patients (4.9%) contrary to what one might have feared. The frequency of SARS-CoV-2 infection in kidney transplant patients is 1.8% nationwide. All regions of France have not been affected in the same way. The prevalence of COVID-19 patients varied by region, reaching up to 10%. The probability of being affected was higher in men and diabetic patients. At October 19, among 3209 infected patients (dialysis and transplant), 573 died from a cause related to SARS-CoV-2. The case fatality in diagnosed cases was 18%. A weekly newsletter has been set up by the Biomedicine Agency using information transmitted by all of the epidemiological support units in the registry. The REIN registry was able to adapt to become a reactive health monitoring tool.
Le registre REIN est un registre national mis en place à la demande des néphrologues et dont le support institutionnel est l’Agence de la biomédecine. Son objectif est le suivi épidémiologique des patients en insuffisance rénale chronique terminale. Ce registre, fort de son expertise et de son réseau national, a su mettre en place très rapidement un suivi épidémiologique des patients dialysés chroniques et/ou greffés atteints par le SARS-CoV-2. Les premiers résultats mettent en évidence une fréquence relativement faible de COVID-19 chez les patients dialysés (4,9 %), contrairement à ce que l’on aurait pu craindre. La fréquence de l’infection SARS-CoV-2 chez les patients transplantés rénaux est de 1,8 % sur l’ensemble du territoire. Toutes les régions de France n’ont pas été touchées de la même manière. La prévalence des patients COVID-19 variait suivant les régions, atteignant 10 % dans la région la plus touchée. La probabilité d’être atteint était plus élevée chez les hommes et chez les patients diabétiques. Au 19 octobre, parmi les 3209 patients infectés (dialysés et transplantés), 573 sont décédés en raison d’une cause liée au SARS-CoV-2. La létalité dans les cas diagnostiqués était de 18 %. Un bulletin d’information hebdomadaire a été mis en place par l’Agence de la biomédecine grâce aux informations transmises par l’ensemble des cellules d’appui épidémiologiques du registre. De ce fait, le registre REIN a pu s’adapter pour devenir un outil réactif de veille sanitaire.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; Coronavirus; Dialyse; Dialysis; Pandémie COVID-19; Renal transplantation; Transplantation rénale.
Copyright © 2021 Société francophone de néphrologie, dialyse et transplantation. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
What does the French REIN registry tell us about Stage 4-5 CKD care in older adults?Front Nephrol. 2023 Jan 17;2:1026874. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2022.1026874. eCollection 2022. Front Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37675001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The essential of 2012 results from the French Renal Epidemiology and Information Network (REIN) ESRD registry.Nephrol Ther. 2015 Apr;11(2):78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2014.08.002. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Nephrol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25457107
-
[REIN Report 2011--summary].Nephrol Ther. 2013 Sep;9 Suppl 1:S3-6. doi: 10.1016/S1769-7255(13)70036-1. Nephrol Ther. 2013. PMID: 24119584 French.
-
Low incidence of SARS-CoV-2, risk factors of mortality and the course of illness in the French national cohort of dialysis patients.Kidney Int. 2020 Dec;98(6):1519-1529. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.07.042. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32858081 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons Learnt during the COVID-19 Pandemic: For Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease, We Should Prioritize Home-Based Treatment and Telemedicine.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2021;46(1):11-16. doi: 10.1159/000512629. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2021. PMID: 33517338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-lasting clinical symptoms 6 months after COVID-19 infection in the French national cohort of patients on dialysis.J Nephrol. 2022 Apr;35(3):787-793. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01295-z. Epub 2022 Mar 16. J Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35294748 Free PMC article.
-
[SFNDT in the heart of the COVID-19 epidemy].Nephrol Ther. 2021 Aug;17(4):200-202. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2021.06.003. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Nephrol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34266784 Free PMC article. French. No abstract available.
-
What data collection methods work best for COVID19 outbreak surveillance for people with end stage kidney disease? An observational cohort study using the UK Renal Registry.BMC Nephrol. 2023 May 8;24(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03148-8. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37158816 Free PMC article.
-
What does the French REIN registry tell us about Stage 4-5 CKD care in older adults?Front Nephrol. 2023 Jan 17;2:1026874. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2022.1026874. eCollection 2022. Front Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37675001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Organisation mondiale de la santé (OMS) 2020. WHO. Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on Covid-19, 2020.http://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-rem...
-
- Fouillet A. Santé publique France; Saint-Maurice: 2020. Surveillance de la mortalité au cours de l’épidémie de Covid-19 du 2 mars au 31 mai 2020 en France.
-
- Covid-19 Task Force Committee of the Japanese Association of Dialysis Physicians, Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy, Japanese Society of Nephrology, Kikuchi K., Nangaku M., Ryuzaki M. Covid-19 of dialysis patients in Japan: current status and guidance on preventive measures. Ther Apher Dial. 2020;24:361–365. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

