Long-Lasting Imprint in the Soluble Inflammatory Milieu Despite Early Treatment of Acute Symptomatic Hepatitis C
- PMID: 33517457
- PMCID: PMC9417126
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab048
Long-Lasting Imprint in the Soluble Inflammatory Milieu Despite Early Treatment of Acute Symptomatic Hepatitis C
Abstract
Background: Treatment with direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection leads to partial restoration of soluble inflammatory mediators (SIMs). In contrast, we hypothesized that early DAA treatment of acute hepatitis C virus (HCV) with DAAs may normalize most SIMs.
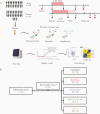
Methods: In this study, we made use of a unique cohort of acute symptomatic hepatitis C patients who cleared HCV with a 6-week course of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir. Plasma samples were used for proximity extension assay measuring 92 proteins.
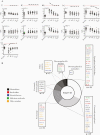
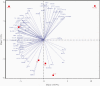
Results: Profound SIM alterations were observed in acute HCV patients, with marked upregulation of interleukin (IL)-6 and CXCL-10, whereas certain mediators were downregulated (eg, monocyte chemoattractant protein-4, IL-7). During treatment and follow-up, the majority of SIMs decreased but not all normalized (eg, CDCP1, IL-18). Of note, SIMs that were downregulated before DAA treatment remained suppressed, whereas others that were initially unchanged declined to lower values during treatment and follow-up (eg, CD244).
Conclusions: Acute hepatitis C was associated with marked changes in the soluble inflammatory milieu compared with both chronic hepatitis patients and healthy controls. Whereas early DAA treatment partly normalized this altered signature, long-lasting imprints of HCV remained.
Keywords: acute infection; direct-acting antivirals; hepatitis C virus; proximity extension assay; soluble inflammatory milieu.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures


References
-
- Wedemeyer H, Dore GJ, Ward JW. Estimates on HCV disease burden worldwide—filling the gaps. J Viral Hepat 2015; 22(Suppl 1):1–5. - PubMed
-
- Wiegand J, Deterding K, Cornberg M, Wedemeyer H. Treatment of acute hepatitis C: the success of monotherapy with (pegylated) interferon alpha. J Antimicrob Chemother 2008; 62:860–5. - PubMed
-
- Deterding K, Grüner N, Buggisch P, et al. ; Hep-Net Acute HCV-III Study Group . Delayed versus immediate treatment for patients with acute hepatitis C: a randomised controlled non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2013; 13:497–506. - PubMed
-
- Jaeckel E, Cornberg M, Wedemeyer H, et al. ; German Acute Hepatitis C Therapy Group . Treatment of acute hepatitis C with interferon alfa-2b. N Engl J Med 2001; 345:1452–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

