Recombinase-aided amplification-lateral flow dipstick assay-a specific and sensitive method for visual detection of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus
- PMID: 33518305
- PMCID: PMC7936119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.12.008
Recombinase-aided amplification-lateral flow dipstick assay-a specific and sensitive method for visual detection of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus
Abstract
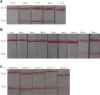
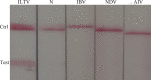
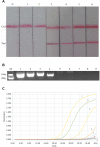
The purpose of this study was to explore a specific, simple, and sensitive method for diagnosis of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Recombinase-aided amplification (RAA) and lateral flow dipstick (LFD) were combined for labeling the optimized RAA probe with 6-carboxyfluorescein (FAM) and the 5'-end of the downstream primer with biotin, respectively. By optimizing the reaction time, temperature, and primer concentration of RAA, a RAA-LFD assay, which could be used for detection of infectious laryngotracheitis, was established. After the specificity and sensitivity test, the target gene fragments could be amplified by RAA-LFD assay in 20 min under isothermal conditions (37°C), and the amplification products could be visually observed and determined by LFD within 3 min. There was no cross-reaction with nucleic acids of other avian pathogens, the lowest detectable limit of RAA-LFD was 102 copies/μL, and the sensitivity of this method was 100 times higher than that of conventional PCR with the lowest detectable limit of 104 copies/μL. The results showed that RAA-LFD assay was highly sensitive, easy to use, and more suitable for clinical detection.
Keywords: avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus; lateral flow dipstick; recombinase-aided amplification.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishment of reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification-lateral-flow dipstick and real-time fluorescence-based reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification methods for detection of the Newcastle disease virus in chickens.Poult Sci. 2020 Jul;99(7):3393-3401. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.03.018. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32616233 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay combined with a lateral flow dipstick for detection of avian infectious bronchitis virus.Poult Sci. 2020 Jan;99(1):89-94. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez559. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32416856 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and visual detection of Mycoplasma synoviae by recombinase-aided amplification assay combined with a lateral flow dipstick.Poult Sci. 2022 Jul;101(7):101860. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101860. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35537343 Free PMC article.
-
Research Note: Rapid detection of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus with real-time fluorescence-based recombinase-aided amplification.Poult Sci. 2020 Oct;99(10):4809-4813. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.06.025. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32988516 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental study on the detection of Gastrodia elata by enzymatic recombinase amplification and immunochromatography.Anal Biochem. 2024 Nov;694:115618. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2024.115618. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Anal Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39009105 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Virus Detection Techniques Based on Recombinant Polymerase Amplification.Molecules. 2024 Oct 21;29(20):4972. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204972. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel rapid visual detection assay for Toxoplasma gondii combining recombinase-aided amplification and lateral flow dipstick coupled with CRISPR-Cas13a fluorescence (RAA-Cas13a-LFD).Parasite. 2022;29:21. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2022021. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Parasite. 2022. PMID: 35420541 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Identification of a Multispecies Carinatae Birds by Chicken EE0.6 Gene Using Real-Time Recombinase-Aid Amplification Assay.Ecol Evol. 2024 Nov 19;14(11):e70551. doi: 10.1002/ece3.70551. eCollection 2024 Nov. Ecol Evol. 2024. PMID: 39563704 Free PMC article.
-
Duplex recombinase aided amplification-lateral flow dipstick assay for rapid distinction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Oct 10;14:1454096. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1454096. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39450337 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid visual detection of anisakid nematodes using recombinase polymerase amplification and SYBR Green I.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 2;13:1026129. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1026129. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36532447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen C., Li X.N., Li G.X., Zhao L., Duan S.X., Yan T.F., Feng Z.S., Ma X.J. Use of a rapid reverse-transcription recombinaseaidedamplification assay for respiratory syncytial virus detection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2018;90:90–95. - PubMed
-
- Lu B., Cheng H.R., Yan Q.F., Huang Z.J., Shen G.F., Zhang Z.F., Li Y., Deng Z.X., Lin M., Cheng Q. Rapid amplification of nucleic acid by recombinant enzyme-mediated amplification technology. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010;40:983–988.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

