The effects of in ovo nicotinamide riboside dose on broiler myogenesis
- PMID: 33518322
- PMCID: PMC7936221
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.12.024
The effects of in ovo nicotinamide riboside dose on broiler myogenesis
Abstract
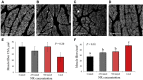
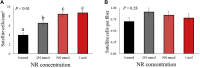
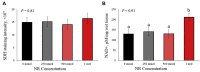
The objective of this study was to determine the effects of in ovo injection of nicotinamide riboside (NR) on broiler embryonic myogenesis. Fertilized Cobb 500 broiler eggs (N = 240) were sorted by weight and within each strata, randomly assigned to 1 of 4 NR dose treatments (0 mmol, 250 mmol, 500 mmol, or 1 mol; final concentration in yolk of 0, 2.5, 5.0, or 10.0 mmol) of NR. At day 10 of incubation, 100 μL of the assigned NR dose was injected into the yolk sac of the developing embryo, and chicks were euthanized within 24 h of hatching. Pectoralis major muscle (PMM) and individual fiber morphometrics were collected. Chicks injected with NR had greater PMM weight and length (P < 0.01), but did not differ from each other (P > 0.14). Chicks from eggs injected with NR had greater PMM weight and width than control chicks (P < 0.01), but did not differ from each other (P = 0.86). Chicks from eggs injected with 500 mmol NR had greater PMM depth than control and 1M chicks (P < 0.04), which did not differ (P = 0.24) from each other. Chicks from eggs injected with 250 mmol NR did not differ in PMM length compared with all other treatments (P > 0.06). There was no treatment effect (P = 0.20) for PMM fiber cross-sectional area; however, there was a treatment effect (P < 0.01) for muscle fiber density. Chicks from eggs injected with 1 mol NR had greater fiber density than all other treatments (P < 0.01). Chicks injected with 250 and 500 mmol NR had greater fiber density than control chicks (P < 0.01), but did not differ (P < 0.06) from each other. Injecting developing embryos at day 10 of incubation increased hatched chick PMM morphometrics, which were partly because of the NR catalyzed increase in muscle fiber density.
Keywords: broiler; muscle fiber; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; nicotinamide riboside; pectoralis major.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Murrani W.K. Effect of injecting amino acids into the egg on embryonic and subsequent growth in the domestic fowl. Br. Poult. Sci. 1982;23:171–174. - PubMed
-
- Bhanja S.K., Mandal A.B., Agarwal S.K., Majumdar S. Effect of in ovo Glucose injection on the post hatch-growth, Digestive Organ development and Blood Biochemical profiles in broiler chickens. Ind. J. Anim. Sci. 2008;78:869–872.
-
- Bieganowski P., Brenner C. Discoveries of nicotinamide riboside as a nutrient and conserved NRK genes establish a Preiss-Handler independent route to NAD+ in fungi and humans. Cell. 2004;117:495–502. - PubMed
-
- Biressi S., Molinaro M., Cossu G. Cellular heterogeneity during vertebrate skeletal muscle development. Dev. Biol. 2007;308:281–293. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

