Knockdown of NIR Suppresses Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation via Promoting FOXO3
- PMID: 33519211
- PMCID: PMC7837597
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S287464
Knockdown of NIR Suppresses Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation via Promoting FOXO3
Abstract
Background: Novel inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase repressor (NIR), a corepressor with a novel inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase (INHAT) activity, has been reported to be a negative modulator of p53 and a regulator of the cell cycle in cancer cells. However, the role of NIR in the progression of breast cancer remains elusive.
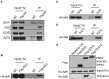
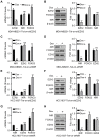
Materials and methods: Oncomine database was used to analyze the mRNA levels and prognosis value of NIR in breast cancer. We performed loss-of-function and gain-of-function studies using lentivirus expressing shRNA targeting NIR, enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) and forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) or lentivirus expressing NIR or FOXO3, respectively. Cell proliferation and colony formation assays were performed. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and immunoprecipitation (IP) were performed to identify the interaction between NIR and polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) subunits. ChIP assay was used to identify the enrichment of NIR, EZH2, H3K27ac and H3K27me3 at the FOXO3 promoter region and the regulation of H3K27 modification at the FOXO3 promoter by NIR.
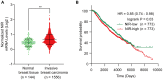
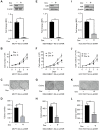
Results: High levels of NIR expression were correlated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Knockdown of NIR suppressed the proliferation of breast cancer cells. Mechanically, NIR was recruited by EZH2 to the promoter vicinity of FOXO3 via direct protein-protein interaction. Silencing NIR increased H3K27ac and decreased H3K27me3 levels at the FOXO3 promoter, resulting in enhancing FOXO3 expression. In accordance with this, growth inhibition of breast cancer cells caused by silencing of NIR could be reversed by FOXO3 knockdown.
Conclusion: NIR knockdown inhibited proliferation by switching the H3K27me3 and H3K27ac marks at the FOXO3 promoter to promote FOXO3 transcription, and this effect depends on the physical interaction between NIR and PRC2 in breast cancer cells. Our results suggest that NIR might be a potential target for breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Breast cancer; EZH2; FOXO3; NIR; PRC2.
© 2021 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors proclaim no conflict of interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
BRCA1 positively regulates FOXO3 expression by restricting FOXO3 gene methylation and epigenetic silencing through targeting EZH2 in breast cancer.Oncogenesis. 2016 Apr 4;5(4):e214. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2016.23. Oncogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27043660 Free PMC article.
-
The EZH2- H3K27me3-DNMT1 complex orchestrates epigenetic silencing of the wwc1 gene, a Hippo/YAP pathway upstream effector, in breast cancer epithelial cells.Cell Signal. 2018 Nov;51:243-256. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.08.011. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 30121333
-
EZH2 and histone deacetylase inhibitors induce apoptosis in triple negative breast cancer cells by differentially increasing H3 Lys27 acetylation in the BIM gene promoter and enhancers.Oncol Lett. 2017 Nov;14(5):5735-5742. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6912. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29113202 Free PMC article.
-
Structural assembly of Polycomb group protein and Insight of EZH2 in cancer progression: A review.J Cancer Res Ther. 2021 Apr-Jun;17(2):311-326. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_1090_19. J Cancer Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33063698 Review.
-
Targeting EZH2 as cancer therapy.J Biochem. 2021 Sep 22;170(1):1-4. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvab007. J Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33479735 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the Fox Gene in Breast Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 7;26(4):1415. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041415. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel INHAT repressor drives glioblastoma growth by promoting ribosomal DNA transcription in glioma stem cells.Neuro Oncol. 2023 Aug 3;25(8):1428-1440. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noac272. Neuro Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36521011 Free PMC article.
-
A narrative review of epigenetic marker in H3K27ac and its emerging potential as a therapeutic target in cancer.Epigenomics. 2025 Mar;17(4):263-279. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2025.2460900. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Epigenomics. 2025. PMID: 39981972 Review.
-
Unmasking the biological function and regulatory mechanism of NOC2L: a novel inhibitor of histone acetyltransferase.J Transl Med. 2023 Jan 17;21(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-03877-2. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36650543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

