In-silico network-based analysis of drugs used against COVID-19: Human well-being study
- PMID: 33519272
- PMCID: PMC7825994
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.01.006
In-silico network-based analysis of drugs used against COVID-19: Human well-being study
Abstract
Introduction: Researchers worldwide with great endeavor searching and repurpose drugs might be potentially useful in fighting newly emerged coronavirus. These drugs show inhibition but also show side effects and complications too. On December 27, 2020, 80,926,235 cases have been reported worldwide. Specifically, in Pakistan, 471,335 has been reported with inconsiderable deaths.
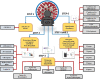
Problem statement: Identification of COVID-19 drugs pathway through drug-gene and gene-gene interaction to find out the most important genes involved in the pathway to deal with the actual cause of side effects beyond the beneficent effects of the drugs.
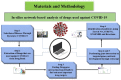
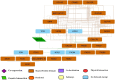
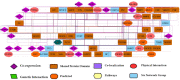
Methodology: The medicines used to treat COVID-19 are retrieved from the Drug Bank. The drug-gene interaction was performed using the Drug Gene Interaction Database to check the relation between the genes and the drugs. The networks of genes are developed by Gene MANIA, while Cytoscape is used to check the active functional association of the targeted gene. The developed systems cross-validated using the EnrichNet tool and identify drug genes' concerned pathways using Reactome and STRING.
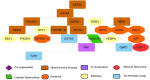
Results: Five drugs Azithromycin, Bevacizumab, CQ, HCQ, and Lopinavir, are retrieved. The drug-gene interaction shows several genes that are targeted by the drug. Gene MANIA interaction network shows the functional association of the genes like co-expression, physical interaction, predicted, genetic interaction, co-localization, and shared protein domains.
Conclusion: Our study suggests the pathways for each drug in which targeted genes and medicines play a crucial role, which will help experts in-vitro overcome and deal with the side effects of these drugs, as we find out the in-silico gene analysis for the COVID-19 drugs.
Keywords: COVID-19; Drug-interactions; Gene-analysis; Interaction networks; Pathways.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Arabi Y.M., Alothman A., Balkhy H.H., Al-Dawood A., AlJohani S., Al Harbi S., Kojan S., Al Jeraisy M., Deeb A.M., Assiri A.M., Al-Hameed F., AlSaedi A., Mandourah Y., Almekhlafi G.A., Sherbeeni N.M., Elzein F.E., Memon J., Taha Y., Almotairi A., Taif J.S. Treatment of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome with a combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and interferon-β1b (MIRACLE trial): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2018;19(1):1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2427-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Browning D.J. Hydroxychloroquine and Chloroquine Retinopathy. 2014. Hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine retinopathy. - DOI
-
- Cao B., Wang Y., Wen D., Liu W., Wang J., Fan G., Ruan L., Song B., Cai Y., Wei M., Li X., Xia J., Chen N., Xiang J., Yu T., Bai T., Xie X., Zhang L., Li C., Wang C. A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382(19):1787–1799. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001282. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

