Development of a Novel Chimeric Endolysin, Lys109 With Enhanced Lytic Activity Against Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 33519773
- PMCID: PMC7843465
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.615887
Development of a Novel Chimeric Endolysin, Lys109 With Enhanced Lytic Activity Against Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
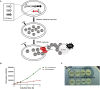
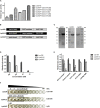
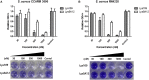
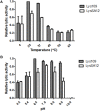
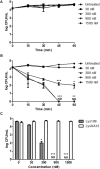
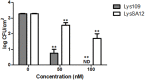
As the incidence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has become increased, phage endolysins are believed as one of the promising alternatives to antibiotics. However, the discovery of potent endolysin is still challenging because it is labor intensive and difficult to obtain a soluble form with high lytic activity. In this respect, the modular structures of Gram-positive endolysins can provide an opportunity to develop novel endolysins by domain rearrangement. In this study, a random domain swapping library of four different endolysins from phages infecting Staphylococcus aureus was constructed and screened to obtain engineered endolysins. The novel chimeric endolysin, Lys109 was selected and characterized for its staphylolytic activity. Lys109 exhibited greater bacterial cell lytic activity than its parental endolysins against staphylococcal planktonic cells and biofilms, showing highly improved activity in eliminating S. aureus from milk and on the surface of stainless steel. These results demonstrate that a novel chimeric endolysin with higher activity and solubility can be developed by random domain swapping and that this chimeric endolysin has a great potential as an antimicrobial agent.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; antimicrobial agent; domain swapping; endolysin; screening.
Copyright © 2021 Son, Kong, Lee and Ryu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Becker S. C., Foster-Frey J., Stodola A. J., Anacker D., Donovan D. M. (2009b). Differentially conserved staphylococcal SH3b_5 cell wall binding domains confer increased staphylolytic and streptolytic activity to a streptococcal prophage endolysin domain. Gene 443 32–41. 10.1016/j.gene.2009.04.023 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

