Antivirulence Strategies for the Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infections: A Mini Review
- PMID: 33519793
- PMCID: PMC7840885
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.632706
Antivirulence Strategies for the Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Infections: A Mini Review
Abstract
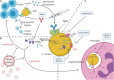
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive bacterium capable of infecting nearly all host tissues, causing severe morbidity and mortality. Widespread antimicrobial resistance has emerged among S. aureus clinical isolates, which are now the most frequent causes of nosocomial infection among drug-resistant pathogens. S. aureus produces an array of virulence factors that enhance in vivo fitness by liberating nutrients from the host or evading host immune responses. Staphylococcal virulence factors have been identified as viable therapeutic targets for treatment, as they contribute to disease pathogenesis, tissue injury, and treatment failure. Antivirulence strategies, or treatments targeting virulence without direct toxicity to the inciting pathogen, show promise as an adjunctive therapy to traditional antimicrobials. This Mini Review examines recent research on S. aureus antivirulence strategies, with an emphasis on translational studies. While many different virulence factors have been investigated as therapeutic targets, this review focuses on strategies targeting three virulence categories: pore-forming toxins, immune evasion mechanisms, and the S. aureus quorum sensing system. These major areas of S. aureus antivirulence research demonstrate broad principles that may apply to other human pathogens. Finally, challenges of antivirulence research are outlined including the potential for resistance, the need to investigate multiple infection models, and the importance of studying antivirulence in conjunction with traditional antimicrobial treatments.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus – bacteria; accessory gene regulator; antimicrobial resistance; antivirulence; infection; quorum sensing; toxin; virulence.
Copyright © 2021 Ford, Hurford and Cassat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baldry M., Kitir B., Frøkiær H., Christensen S. B., Taverne N., Meijerink M., et al. (2016). The agr Inhibitors Solonamide B and Analogues Alter Immune Responses to Staphylococcus aureus but Do Not Exhibit Adverse Effects on Immune Cell Functions. PLoS One 11:e0145618. 10.1371/journal.pone.0145618 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

