Identifying Candidate Genes Involved in the Regulation of Early Growth Using Full-Length Transcriptome and RNA-Seq Analyses of Frontal and Parietal Bones and Vertebral Bones in Bighead Carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis)
- PMID: 33519908
- PMCID: PMC7844397
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.603454
Identifying Candidate Genes Involved in the Regulation of Early Growth Using Full-Length Transcriptome and RNA-Seq Analyses of Frontal and Parietal Bones and Vertebral Bones in Bighead Carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis)
Abstract
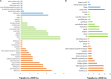
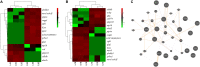
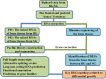
Growth, one of the most important traits monitored in domestic animals, is essentially associated with bone development. To date, no large-scale transcriptome studies investigating bone development in bighead carp have been reported. In this study, we applied Isoform-sequencing technology to uncover the entire transcriptomic landscape of the bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) in early growth stage, and obtained 63,873 non-redundant transcripts, 20,907 long non-coding RNAs, and 1,579 transcription factors. A total of 381 alternative splicing events were seen in the frontal and parietal bones with another 784 events simultaneously observed in the vertebral bones. Coupling this to RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data, we identified 27 differentially expressed unigenes (DEGs) in the frontal and parietal bones and 45 DEGs in the vertebral bones in the fast-growing group of fish, when compared to the slow-growing group of fish. Finally, 15 key pathways and 20 key DEGs were identified and found to be involved in regulation of early growth such as energy metabolism, immune function, and cytoskeleton function and important cellular pathways such as the arginine and proline metabolic pathway (p4ha1), FoxO signaling pathway (sgk1), cell adhesion molecules (b2m, ptprc, and mhcII), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor signaling pathway (scd). We established a novel full-length transcriptome resource and combined it with RNA-seq to elucidate the mechanism of genetic regulation of differential growth in bighead carp. The key DEGs identified in this study could fuel further studies investigating associations between growth and bone development and serve as a source of potential candidate genes for marker-assisted breeding programs.
Keywords: Iso-Seq; bighead carp; differential growth; differentially expressed unigene; full-length transcript.
Copyright © 2021 Luo, Zhou, Wang, Yu and Tong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Beck S. V., Rasanen K., Ahi E. P., Kristjansson B. K., Skulason S., Jonsson Z. O., et al. (2019). Gene expression in the phenotypically plastic Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus): a focus on growth and ossification at early stages of development. Evol. Dev. 21 16–30. 10.1111/ede.12275 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berg M., Agesen T. H., Thiis-Evensen E., Merok M. A., Teixeira M. R., Vatn M. H., et al. (2010). Distinct high-resolution genome profiles of early onset and late onset colorectal cancer integrated with gene expression data identify candidate susceptibility loci. Mol. Cancer 9:100. 10.1186/1476-4598-9-100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

