Comparative Transcriptome Profile Analysis of Longissimus dorsi Muscle Tissues From Two Goat Breeds With Different Meat Production Performance Using RNA-Seq
- PMID: 33519920
- PMCID: PMC7838615
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.619399
Comparative Transcriptome Profile Analysis of Longissimus dorsi Muscle Tissues From Two Goat Breeds With Different Meat Production Performance Using RNA-Seq
Abstract
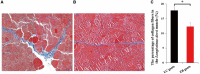
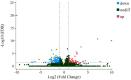
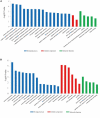
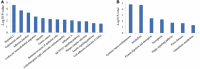
Carcass weight, meat quality and muscle components are important traits economically and they underpin most of the commercial return to goat producers. In this study, the Longissimus dorsi muscle tissues were collected from five Liaoning cashmere (LC) goats and five Ziwuling black (ZB) goats with phenotypic difference in carcass weight, some meat quality traits and muscle components. The histological quantitative of collagen fibers and the transcriptome profiles in the Longissimus dorsi muscle tissues were investigated using Masson-trichrome staining and RNA-Seq, respectively. The percentage of total collagen fibers in the Longissimus dorsi muscle tissues from ZB goats was less than those from LC goats, suggesting that these ZB goats had more tender meat. An average of 15,919 and 15,582 genes were found to be expressed in Longissimus dorsi muscle tissues from LC and ZB goats, respectively. Compared to LC goats, the expression levels of 78 genes were up-regulated in ZB goats, while 133 genes were down-regulated. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses revealed that the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were significantly enriched in GO terms related to the muscle growth and development and the deposition of intramuscular fat and lipid metabolism, hippo signaling pathway and Jak-STAT signaling pathway. The results provide an improved understanding of the genetic mechanisms regulating meat production performance in goats, and will help us improve the accuracy of selection for meat traits in goats using marker-assisted selection based on these differentially expressed genes obtained.
Keywords: Liaoning cashmere goats; RNA-Seq; Ziwuling black goats; differentially expressed gene; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2021 Shen, Hao, Wang, Hu, Liu, Li, Ke, Song, Lu, Hu, Qiao, Wu and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep Small RNA Sequencing Reveals Important miRNAs Related to Muscle Development and Intramuscular Fat Deposition in Longissimus dorsi Muscle From Different Goat Breeds.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jun 13;9:911166. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.911166. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35769318 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of circular RNAs in Longissimus dorsi muscle tissue from two goat breeds using RNA-Seq.Mol Genet Genomics. 2022 May;297(3):817-831. doi: 10.1007/s00438-022-01887-1. Epub 2022 Apr 16. Mol Genet Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35429278
-
Integrated transcriptome analysis reveals roles of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in caprine skeletal muscle mass and meat quality.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Feb 22;23(1):63. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-00987-4. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36810929
-
Advances in the discovery of genetic elements underlying longissimus dorsi muscle growth and development in the pig.Anim Genet. 2023 Dec;54(6):709-720. doi: 10.1111/age.13365. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Anim Genet. 2023. PMID: 37796678 Review.
-
Growth, haemato-biochemical, hormonal and disease characteristics in Black Bengal goats: a review.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2024 Jan 23;56(2):52. doi: 10.1007/s11250-024-03898-z. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2024. PMID: 38253786 Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal Transcriptome Dynamics of Longissimus dorsi Reveals the Mechanism of the Differences in Muscle Development and IMF Deposition between Fuqing Goats and Nubian Goats.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jun 12;14(12):1770. doi: 10.3390/ani14121770. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929389 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of lncRNAs Expression Profile Related to Goat Skeletal Muscle at Different Development Stages.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 6;12(19):2683. doi: 10.3390/ani12192683. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230427 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative and Functional Analysis of miRNAs and mRNAs Involved in Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy of Juvenile and Adult Goats.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 25;14(2):315. doi: 10.3390/genes14020315. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833242 Free PMC article.
-
miR-103-3p Regulates the Proliferation and Differentiation of C2C12 Myoblasts by Targeting BTG2.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15318. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015318. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894995 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Sequencing in Different Types of Goat Skeletal Muscles Reveals Genes Regulating Muscle Development and Meat Quality.Animals (Basel). 2021 Oct 8;11(10):2906. doi: 10.3390/ani11102906. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht E., Komolka K., Will K. (2013). Tissue distribution and blood circulation of agouti signaling protein (ASIP) in relationship with body composition in cattle. Proc. JPN. Soc. Anim. Nutr. Metab. 57 89–95.
-
- Arora R., Naveen Kumar S., Sudarshan S., Fairoze M. N., Kaur M., Sharma A., et al. (2019). Transcriptome profiling of longissimus thoracis muscles identifies highly connected differentially expressed genes in meat type sheep of India. PLoS One 14:e0217461. 10.1371/journal.pone.0217461 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

