Knockdown of RhoC Inhibits Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Invasion and Metastasis via Regulation of HMGA2
- PMID: 33519932
- PMCID: PMC7817318
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6644077
Knockdown of RhoC Inhibits Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Invasion and Metastasis via Regulation of HMGA2
Abstract
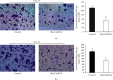
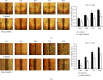
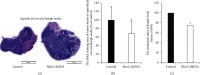
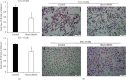
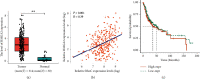
Ras homolog family member C (RhoC) is an important component of intracellular signal transduction and its overexpression has been reported to be involved in regulating tumor proliferation, invasion, and metastasis in various malignant tumors. However, its role and underlying mechanism in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) still remain obscure. In our study, RhoC expression, its relation with clinical stages, and survival rate in OSCC were analyzed using datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Next, a RhoC knockdown cell model was established in vitro, and the effects of RhoC knockdown in OSCC cells were detected by the MTT assay, colony formation assay, transwell invasion assay, scratch assay, and F-actin phalloidin staining. An in vivo tongue-xenografted nude mouse model was established to measure the effects of knockdown of RhoC on tumor cell growth and lymph node metastasis. A mechanism study was conducted by real-time PCR and immunocytochemistry. The results of TCGA analysis showed that RhoC was overexpressed in OSCC tumor tissues. In vitro assays indicated that knockdown of RhoC did not have much effect on OSCC cell growth but significantly suppressed cell colony formation, invasion, and migration abilities, and F-actin polymerization was also reduced. The tongue-xenografted in vivo model demonstrated that knockdown of RhoC suppressed OSCC cell growth and inhibited metastasis to the superficial cervical lymph nodes. Further mechanism studies showed that knockdown of RhoC downregulated HMGA2 expression, and HMGA2 expression was highly correlated with RhoC expression in OSCC tumor tissues via the analysis of TCGA datasets. Overall, our study showed that knockdown of RhoC inhibited OSCC cells invasion and migration in vitro and OSCC cell growth and lymph node metastasis in vivo. Moreover, the potential mechanisms involved in these activities may be related to the regulation of HMGA2 expression. The RhoC gene could serve as a promising therapeutic target for OSCCs in the future.
Copyright © 2021 Feng Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





References
-
- Kim R., Naval-Gías L., Rodríguez-Campo F. J., Sastre-Pérez J., Muñoz-Guerra M. F., Gil-Díez Usandizaga J. L. Contralateral lymph neck node metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: a retrospective analytic study in 315 patients. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 2008;66(7):1390–1398. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2008.01.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Golen K. L., Wu Z. F., Qiao X. T., Wei L., Merajver S. D. RhoC GTPase, a novel transforming oncogene for human mammary epithelial cells that partially recapitulates the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype. International Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2000;60(20):5832–5838. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

