Remote monitoring temporal trends during COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with implanted defibrillators
- PMID: 33520021
- PMCID: PMC7825828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2021.01.005
Remote monitoring temporal trends during COVID-19 pneumonia in patients with implanted defibrillators
Abstract
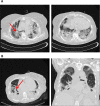
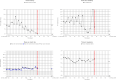
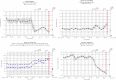
It is unknown whether some of the clinical parameters transmitted by remote monitoring (RM) of cardiac implanted devices could show recurrent patterns caused by COVID-19 infection. Our aim was to describe RM daily temporal trends for implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) or cardiac resynchronization therapy defibrillator (CRT-D) recipients during COVID-19 infection. A 65-year-old woman with a CRT-D had a sudden increase of approximately 15 bpm and 10 bpm in nocturnal and mean heart rate, respectively, 11 days before hospitalization for COVID-19 pneumonia. At the same time physical activity decreased progressively and continuously. A 78-year-old woman with an ICD showed significant changes in RM trends starting from the COVID-19-related symptoms: strong decrease in physical activity, progressive increase in mean and nocturnal heart rate, irregular trend of heart rate variability, and rapid drop in thoracic impedance. Two months later, on hospitalization, computed tomography showed a "crazy-paving" pattern of the lungs, which is a clinical picture of COVID-19 pneumonia with concomitant pleural effusion. <Learning objective: Patients with complications related to the COVID-19 infection appeared to show variations in the remote monitoring (RM) temporal trends of clinical variables daily transmitted from implanted cardiac devices. These changes may not be specific to COVID-19, but owing to the severity of the pandemic, the use of RM to capture patient's condition makes intuitive sense for early diagnosis, intervention, and additional follow-up in this high-risk population.>.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cardiac resynchronization therapy; Implantable cardioverter defibrillator; Remote monitoring; SARS-CoV.
© 2021 Japanese College of Cardiology. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
L.A. and D. G. are employees of BIOTRONIK Italia. All the remaining authors have no major conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of remote monitoring of implanted cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) and cardiac resynchronisation therapy device (CRT-D) patients on healthcare costs in the Silesian population: three-year follow-up.Kardiol Pol. 2017;75(6):573-580. doi: 10.5603/KP.a2017.0019. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Kardiol Pol. 2017. PMID: 28150288
-
The use of remote monitoring of cardiac implantable devices during the COVID-19 pandemic: an EHRA physician survey.Europace. 2022 Mar 2;24(3):473-480. doi: 10.1093/europace/euab215. Europace. 2022. PMID: 34410364 Free PMC article.
-
[Safety and efficacy of classic ambulatory implantable cardioverter-defibrillator and resynchronisation systems follow-up compared to telemetric follow-up].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2016 Mar;40(237):153-9. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2016. PMID: 27088195 Polish.
-
Remote monitoring of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and resynchronization devices to improve patient outcomes: dead end or way ahead?Europace. 2019 Jun 1;21(6):846-855. doi: 10.1093/europace/euz011. Europace. 2019. PMID: 30903152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time trends in sudden cardiac death risk in heart failure patients with cardiac resynchronization therapy: a systematic review.Eur Heart J. 2020 Jun 1;41(21):1976-1986. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz773. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 31750896
Cited by
-
Detecting early physiologic changes through cardiac implantable electronic device data among patients with COVID-19.Cardiovasc Digit Health J. 2022 Oct;3(5):247-255. doi: 10.1016/j.cvdhj.2022.07.070. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Cardiovasc Digit Health J. 2022. PMID: 35942055 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Heart Rate Variability: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies with Control Groups.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 4;20(2):909. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20020909. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36673664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inciardi RM, Adamo M, Lupi L, Cani DS, Di Pasquale M, Tomasoni D, Italia L, Zaccone G, Tedino C, Fabbricatore D, Curnis A, Faggiano P, Gorga E, Lombardi CM, Milesi G. Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 and cardiac disease in Northern Italy. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:1821–1829. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hindricks G, Taborsky M, Glikson M, Heinrich U, Schumacher B, Katz A, Brachmann J, Lewalter T, Goette A, Block M, Kautzner J, Sack S, Husser D, Piorkowski C, Søgaard P. Implant-based multiparameter telemonitoring of patients with heart failure (IN-TIME): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2014;384:583–590. - PubMed
-
- Kaysin A, Viera AJ. Community-acquired pneumonia in adults: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Phys. 2016;94:698–706. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

