When Harry Met Sally: Single-Session INARI FlowTriever and Impella RP
- PMID: 33520023
- PMCID: PMC7817901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2020.10.002
When Harry Met Sally: Single-Session INARI FlowTriever and Impella RP
Abstract
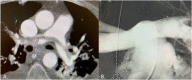
Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy devices have revolutionized the treatment of massive pulmonary embolism (PE) by providing a rapid, non-thrombolytic based method to re-establish right-sided circulation while reducing bleeding complications. However, with massive PE, the acute increase in right ventricular afterload results in a compounded hemodynamic compromise, which may necessitate the need for advanced cardiac support. This case exemplifies the need for a comprehensive and synergistic approach to the management of massive PE. To our knowledge, this is the first report of combination therapy using large bore mechanical suction thrombectomy (FlowTriever, INARI Medical, Irvine, CA, USA) in conjunction with the implantation of right ventricular mechanical support (Impella RP, ABIOMED, Danvers, MA, USA) in an effort to reverse the right ventricular "shock spiral." <Learning objective: To understand the importance of timely intervention in massive pulmonary embolism (PE) and the role of percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy devices in such situations where thrombolysis fails or is contraindicated. To incorporate the simultaneous use of mechanical circulatory support in the setting of massive PE.>.
Keywords: Massive pulmonary embolism; Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy; Right ventricular assist device; Right-sided cardiogenic shock.
© 2020 Japanese College of Cardiology. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Dudzinski D.M., Giri J., Rosenfield K. Interventional treatment of pulmonary embolism. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;10 - PubMed
-
- Tu T., Toma C., Tapson V.F., Adams C., Jaber W.A., Silver M. A prospective, single-arm, multicenter trial of catheter-directed mechanical thrombectomy for intermediate-risk acute pulmonary embolism: the FLARE study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:859–869. - PubMed
-
- Anderson M.B., Goldstein J., Milano C., Morris L.D., Kormos R.L., Bhama J. Benefits of a novel percutaneous ventricular assist device for right heart failure: the prospective RECOVER RIGHT study of The Impella RP device. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015;34:1549–1560. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhury P., Gadre S.K., Schneider E., Renapurkar R.D., Gomes M., Haddadin I. Impact of multidisciplinary pulmonary embolism response team availability on management and outcomes. Am J Cardiol. 2019;124:1465–1469. - PubMed
-
- Kapur N.K., Esposito M.L., Bader Y., Morine K.J., Kiernan M.S., Pham D.T. Mechanical circulatory support devices for acute right ventricular failure. Circulation. 2017;136:314–326. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

