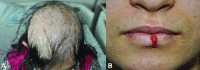
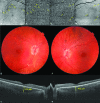
An Unusual Presentation of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada
- PMID: 33520140
- PMCID: PMC7841286
- DOI: 10.18502/jovr.v16i1.8263
An Unusual Presentation of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Read RW, Holland GN, Rao NA, Tabbara KF, Ohno S, Arellanes-Garcia L, et al. Revised diagnostic criteria for Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease: report of an international committee on nomenclature. Am J Ophthalmol 2001;131:647–652. - PubMed
-
- DiPreta EA, Smith KJ, Williams J, Skelton H. Histopathologic findings in the alopecia associated with Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. J Cutan Med Surg 2000;4:155–159. - PubMed
-
- Yang P, Zhong Y, Du L, Chi W, Chen L, Zhang R, et al. Development and evaluation of diagnostic criteria
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
