Catalytic Mechanism of Non-Target DNA Cleavage in CRISPR-Cas9 Revealed by Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics
- PMID: 33520346
- PMCID: PMC7842700
- DOI: 10.1021/acscatal.0c03566
Catalytic Mechanism of Non-Target DNA Cleavage in CRISPR-Cas9 Revealed by Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics
Abstract
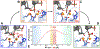
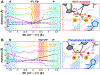
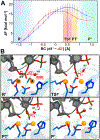
CRISPR-Cas9 is a cutting-edge genome editing technology, which uses the endonuclease Cas9 to introduce mutations at desired sites of the genome. This revolutionary tool is promising to treat a myriad of human genetic diseases. Nevertheless, the molecular basis of DNA cleavage, which is a fundamental step for genome editing, has not been established. Here, quantum-classical molecular dynamics (MD) and free energy methods are used to disclose the two-metal-dependent mechanism of phosphodiester bond cleavage in CRISPR-Cas9. Ab initio MD reveals a conformational rearrangement of the Mg2+-bound RuvC active site, which entails the relocation of H983 to act as a general base. Then, the DNA cleavage proceeds through a concerted associative pathway fundamentally assisted by the joint dynamics of the two Mg2+ ions. This clarifies previous controversial experimental evidence, which could not fully establish the catalytic role of the conserved H983 and the metal cluster conformation. The comparison with other two-metal-dependent enzymes supports the identified mechanism and suggests a common catalytic strategy for genome editing and recombination. Overall, the non-target DNA cleavage catalysis described here resolves a fundamental open question in the CRISPR-Cas9 biology and provides valuable insights for improving the catalytic efficiency and the metal-dependent function of the Cas9 enzyme, which are at the basis of the development of genome editing tools.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; QM/MM; free energy simulations; genome editing; magnesium-aided catalysis; non-coding RNA; phosphodiester bond cleavage; protein/nucleic acid interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
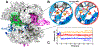
References
-
- Doudna JA; Charpentier E Genome Editing. The New Frontier of Genome Engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science 2014, 346, 1258096. - PubMed
-
- Stadtmauer EA; Fraietta JA; Davis MM; Cohen AD; Weber KL; Lancaster E; Mangan PA; Kulikovskaya I; Gupta M; Chen F; Tian L; Gonzalez VE; Xu J; Jung I; Melenhorst JJ; Plesa G; Shea J; Matlawski T; Cervini A; Gaymon AL; Desjardins S; Lamontagne A; Salas-Mckee J; Fesnak A; Siegel DL; Levine BL; Jadlowsky JK; Young RM; Chew A; Hwang W; Hexner EO; Carreno BM; Nobles CL; Bushman FD; Parker KR; Qi Y; Satpathy AT; Chang HY; Zhao Y; Lacey SF; June CH CRISPR-Engineered T Cells in Patients with Refractory Cancer. Science 2020, 367, eaba7365. - PMC - PubMed
