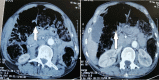
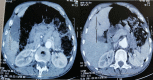
Sigmoid Colon Tuberculosis Revealed by a Perforation and Peritonitis
- PMID: 33520488
- PMCID: PMC7834544
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12272
Sigmoid Colon Tuberculosis Revealed by a Perforation and Peritonitis
Abstract
Intestinal tuberculosis is a frequent disease in developing countries, causing considerable morbidity and mortality. However, tuberculosis of the colon is rarer, and it also appears to be more common in immunosuppressed patients. We report the case of a 71-year-old immunocompetent man who was admitted to the emergency department with an acute abdomen and features of perforation peritonitis. A sigmoid perforation on cancer was suspected on computed tomography (CT) scan and surgical exploration. A standard sigmoidectomy with end colostomy (Hartmann's procedure) and peritoneal toileting was done. The pathological assessment of the surgical specimen revealed the sigmoid colon tuberculosis, complicated by perforation and peritonitis. Thus, the unexpected diagnosis of sigmoid colon tuberculosis was only made after the histopathological examination. Then, he received anti-tuberculosis treatment for six months. Therefore, a complete colonoscopy was performed at the end of the treatment, which returned to be normal. Thereafter, the restoration of intestinal continuity was performed. Colon tuberculosis is a rare disease and even rarer in people without immunodeficiency or on immunosuppressive therapy. If diverticulitis is the most common cause of sigmoid perforation, sigmoid perforation because of tuberculosis is extremely rare. However, an isolated primary sigmoid perforation of tubercular origin is not reported. We report this exceptional case of sigmoid colon tuberculosis complicated by perforation and generalized peritonitis to sensitize the medical team to its rare occurrence, which will be of paramount importance due to the increasing incidence of tuberculosis worldwide.
Keywords: colon perforation; peritonitis; sigmoid tuberculosis; sigmoidectomy; surgical case reports.
Copyright © 2020, Ait Ali et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2014. [Dec;2020 ];http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/137094/1/9789241564809_eng.pdf 2014
-
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in solid-organ transplant recipients: impact and implications for management. Singh N, Paterson DL. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;27:1266–1277. - PubMed
-
- Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Sharma SK, Mohan A. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15520485/ Indian J Med Res. 2004;120:316–353. - PubMed
-
- Dawson A. In: Bockus Gastroenterology. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1995. The respiratory system; pp. 3404–3419.
-
- Gorbach S. In: Gastrointestinal Diseases. Vol. 2. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1989. Tuberculosis of the gastrointestinal tract; pp. 363–372.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources